
Biochemistry Answer Hexokinase Click the link in our bio for an
SUMMARY. The first step in metabolism of glucose (Glc) is usually phosphorylation,catalyzed by hexokinase. However, the Glc-6-P produced can then enter one or more of several alternative pathways. Selective expression of isozymic forms of hexokinase, differing in catalytic and regulatory properties as well as subcellular localization, is likely to be an important factor in determining the.

Glycolysis Hexokinase vs Glucokinase [free sample] YouTube
Our data on hexokinase and glucokinase expression point out an absence of cross regulation mechanisms at the transcription level and different regulatory pathways. In the presence of glucose, CaHxk2 migrates in the nucleus and contributes to the glucose repression signaling pathway. In addition, CaHxk2 participates to oxidative, osmotic and.

Glucokinase vs Hexokinase Glycogenesis Glycolytic Enzymes Dr
Hexokinase II (HK-II) is a predominant isoform in insulin-sensitive tissues such as heart, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissues.. Glucokinase has a molecular mass of ~50 kDa while HK-I,.

Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase YouTube
Glucokinase (GCK or hexokinase IV) (see Glossary) plays a critical role in glucose homeostasis. In pancreatic beta-cells it ensures that insulin secretion is matched to the circulating blood glucose level, in the liver it facilitates glycogen storage and the post-prandial clearance of glucose from the bloodstream, and in certain neurones and neuroendocrine cells it mediates glucose sensing.
What is the differences between hexokinase and glucokinase? Medical
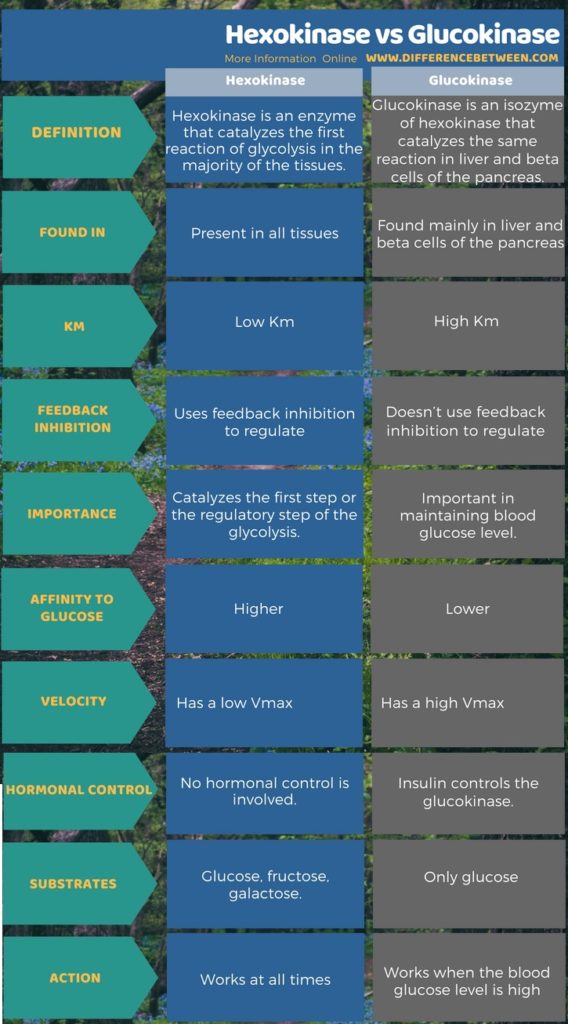
This video provides a tutorial on important difference between hexokinase and glucokinase enzyme. Hexokinase enzyme has low Km (0.1 mM, high affinity for sub.
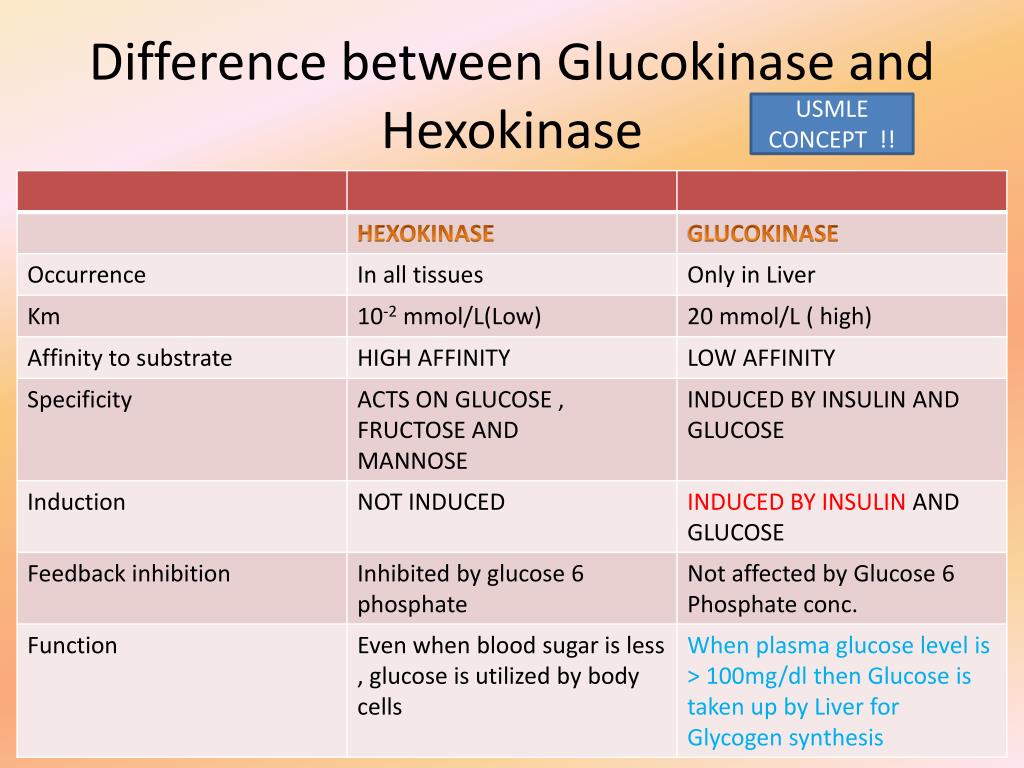
10 Difference between Hexokinase and Glucokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that irreversibly phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate.In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokinase possesses the ability to transfer an inorganic phosphate group from ATP to a substrate. Hexokinases should not be confused with glucokinase.
Difference Between Hexokinase and Glucokinase Compare the Difference
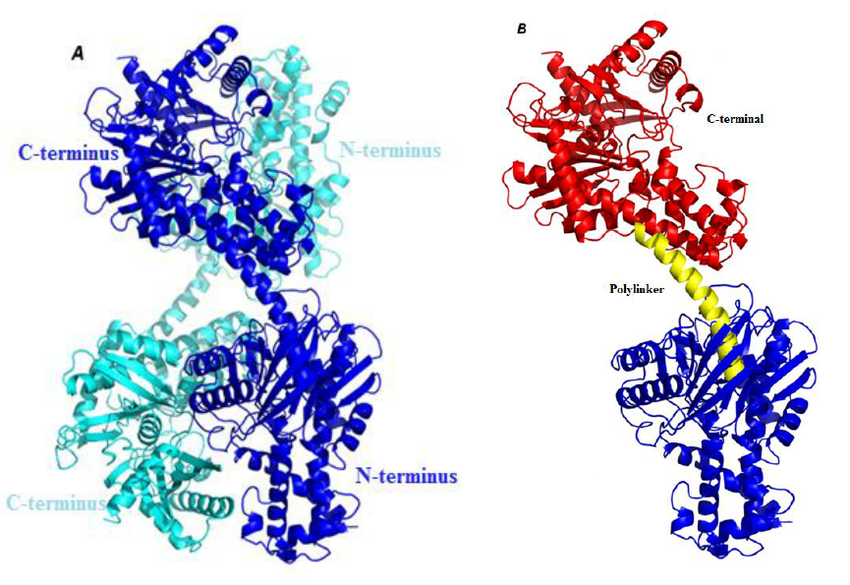
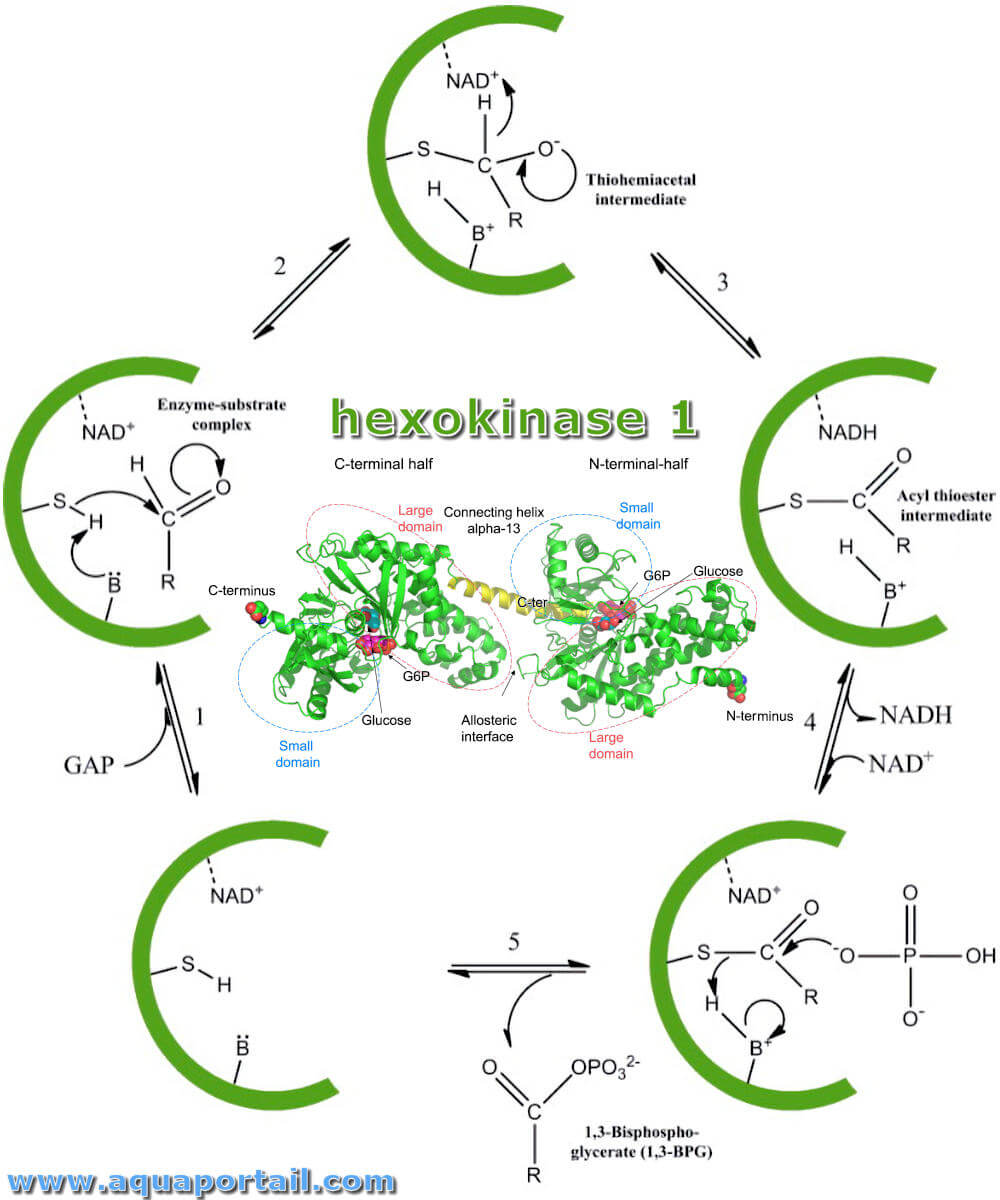
1.1. Structure and function of GK. GK, termed hexokinase 4, is a member of the hexokinase family Citation 1, Citation 2.It is an inducible enzyme composed of 465 amino acids with a molecular mass of ∼52 kDa Citation 3.The three-dimensional structure of GK can be divided into three parts: large, small, and connected domains (Figure 1).The connected domain is composed of three segments of.
Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase Definition, Mechanism And Function
Hexokinase Vs. Glucokinase. While the heading of this subsection may suggest that these two work in opposition to one another, they are in fact very similar and basically perform the same function. Hexokinase is actually a broader term for a class of enzymes that phosphorylates six-carbon sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose etc.), while.
PPT Glycolysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6955097
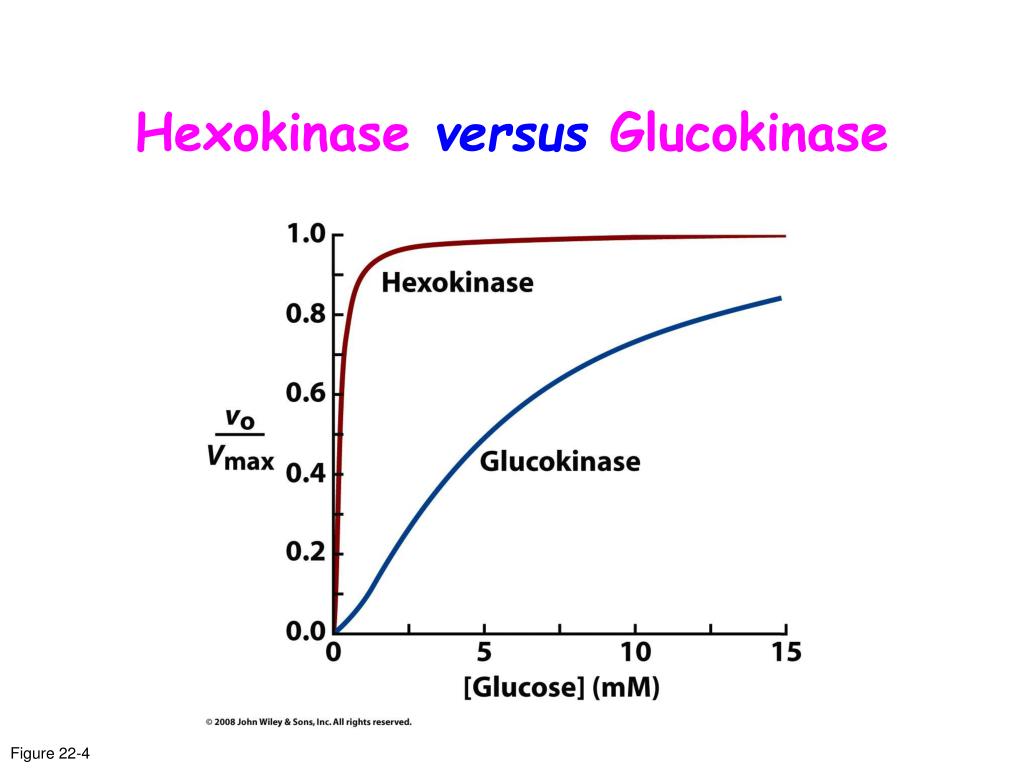
Glucokinase Versus Hexokinase. Hexokinase exists in two different isoforms that have different kinetic and regulatory properties (Table 6-1). Glucokinase, the isoform in liver, has kinetic properties that allow it to capture much of the dietary glucose that enters the liver from the intestines via the portal circulation. This high-capacity.

Hexokinase vs Glucokinase What Is The Difference YouTube
Hexokinase/Glucokinase. E Van Schaftingen, in Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry (Second Edition), 2013. Subcellular Localization of Mammalian Hexokinases. Hexokinases are cytosolic enzymes, but hexokinases I and II bind to mitochondria through a N-terminal hydrophobic region that interacts with voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). VDAC, a porin present in the outer mitochondrial membrane.

Biochemistry Glossary Hexokinase vs. Glucokinase Draw It to Know It
A search of "skeletal muscle" and the glucose phosphorylation isozyme "hexokinase II" and "hexokinase 2" returned only 199 published papers. The case is made that glucose phosphorylation by hexokinase II is an important determinant of the rate of insulin-stimulated muscle glucose uptake in vivo and contributes to insulin resistance.
Hexokinase définition et explications
Glucokinase / metabolism Hexokinase / genetics* Hexokinase / metabolism Humans Isoenzymes / genetics* Isoenzymes / metabolism Molecular Structure Sequence Homology, Nucleic Acid.

Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase Importance and Clinical Significance YouTube
Hexokinase IV or Glucokinase is specifically expressed within the liver and pancreas. HKIV is cytoplasmic and not tethered to the mitochondria. Activity within the pancreas serves as a sensor for the release of insulin, and in the liver for the production of G6P that will fuel glycogen production. HKIV has a higher Km than HKI and HKII, thus it.

Difference Between Hexokinase and Glucokinase
Energy Metabolism | Hexokinase/Glucokinase☆ Emile Van Schaftingen, in Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry (Third Edition), 2021. Hexokinase 4 (Glucokinase) Low Affinity for Glucose and Sigmoidal Kinetics (Fig. 4)Glucokinase is characterized by a low affinity for glucose. The concentration at which 50% activity is reached is about 8 mM for the human enzyme.
PPT Basic Concepts in Metabolism and Regulation of Blood sugar levels
Moonlighting proteins are defined as proteins with two or more functions that are unrelated and independent to each other, so that inactivation of one of them should not affect the second one and vice versa. Intriguingly, all the glycolytic enzymes are described as moonlighting proteins in some organisms. Hexokinase (HXK) is a critical enzyme.

Hexokinase vs. Glucokinase YouTube
Glucokinase: liver and β-cells of the pancreas have a lower affinity for glucose than hexokinases of other tissues. Low glycemia (portal blood): Glucose is available to extrahepatic tissue. High glycemia (portal blood): Glucose enters the liver and is stored as glycogen. PFK-1; Pyruvate kinase; PFK-1 and hexokinase/glucokinase require ATP.