
Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes Vidyakul
The crucial events in aerobic respiration are: Complete oxidation of pyruvate by stepwise removal of all the hydrogen atoms, leaving 3 CO2 molecules. It takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. Passing on of electrons removed as part of H-atoms to molecular O2 with simultaneous synthesis of ATP. It occurs on the inner membrane of mitochondria.

Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes Vidyakul
Anaerobic respiration occurs in organisms like yeast, certain bacteria, and parasitic worms. The animals and plants that can exist and gain energy even in the lack of oxygen are called Anaerobic. Glucose Alcohol + CO2 + (Energy) Yeast is known to be a single-celled fungus.
Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes Leverage Edu
CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology CHAPTER-14 Respiration in Plants class 11 Notes Biology Respiration is an energy releasing, enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of food substance inside living cells.
Mind Map Respiration in Plants Notes EduRev
Free Shipping on eBay! Shop for Plants now
PPT Plant Respiration PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9653205
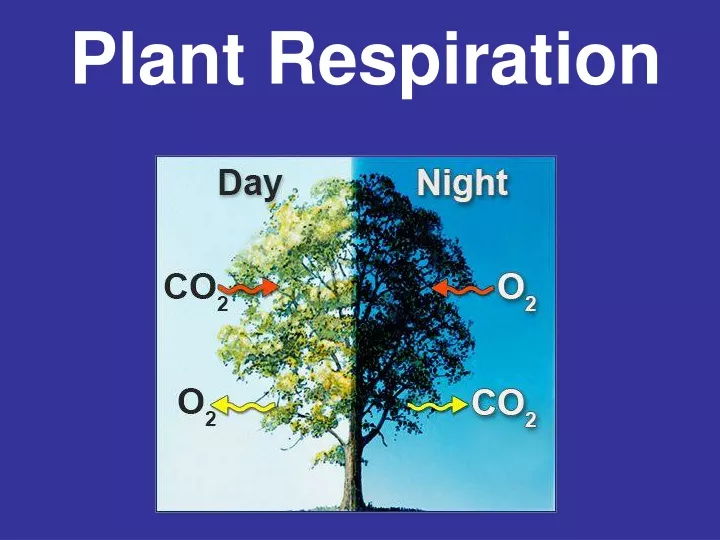
In normal respiration of plants, O 2 is utilised to breakdown carbohydrates into CO 2, H 2 O and energy as by-products. This energy is used for other body processes. In cases where sufficient oxygen is not available, there is partial oxidation of glucose to form pyruvic acid. This process is called glycolysis.

Respiration in Plants Revision Notes for NEET Entrance Exam
The breaking of the C-C bonds of the substrates (complex compounds) through oxidation within the cells, leading to. release of a considerable amount of energy, is known as respiration. The process of respiration occurs inside a living cell. Hence, this process is also known as cellular respiration. Location of respiration: Cytoplasm and.

Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes Vidyakul
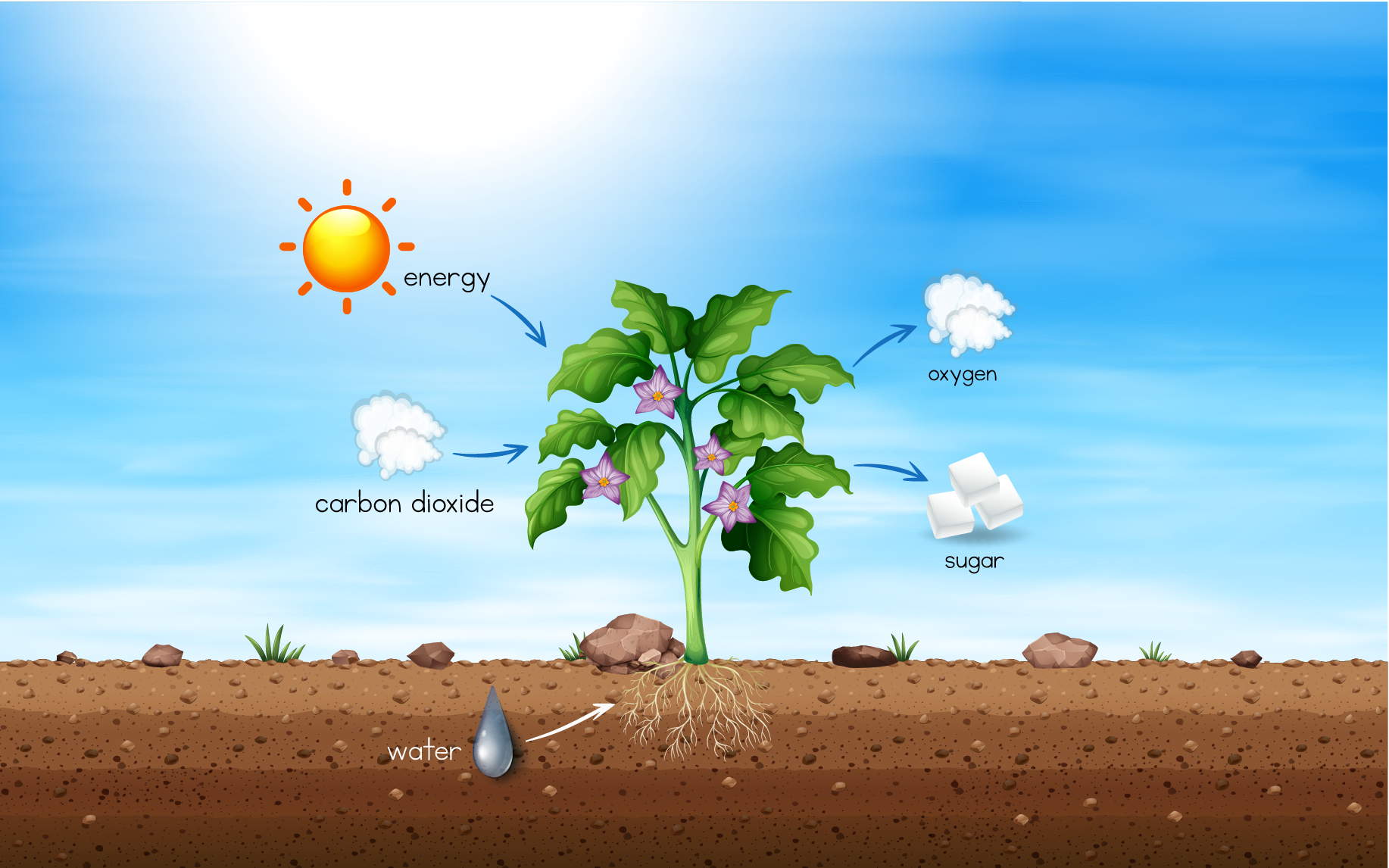
Respiration or Cellular respiration in plants is a catabolic process that involves the oxidation or breakdown of complex molecules into simple molecules. For example, the breakdown of glucose in presence of oxygen to release carbon-dioxide, water and energy. Fig.1. Breakdown of Glucose

* Respiration in plants capture notes You guys will learn a lot from
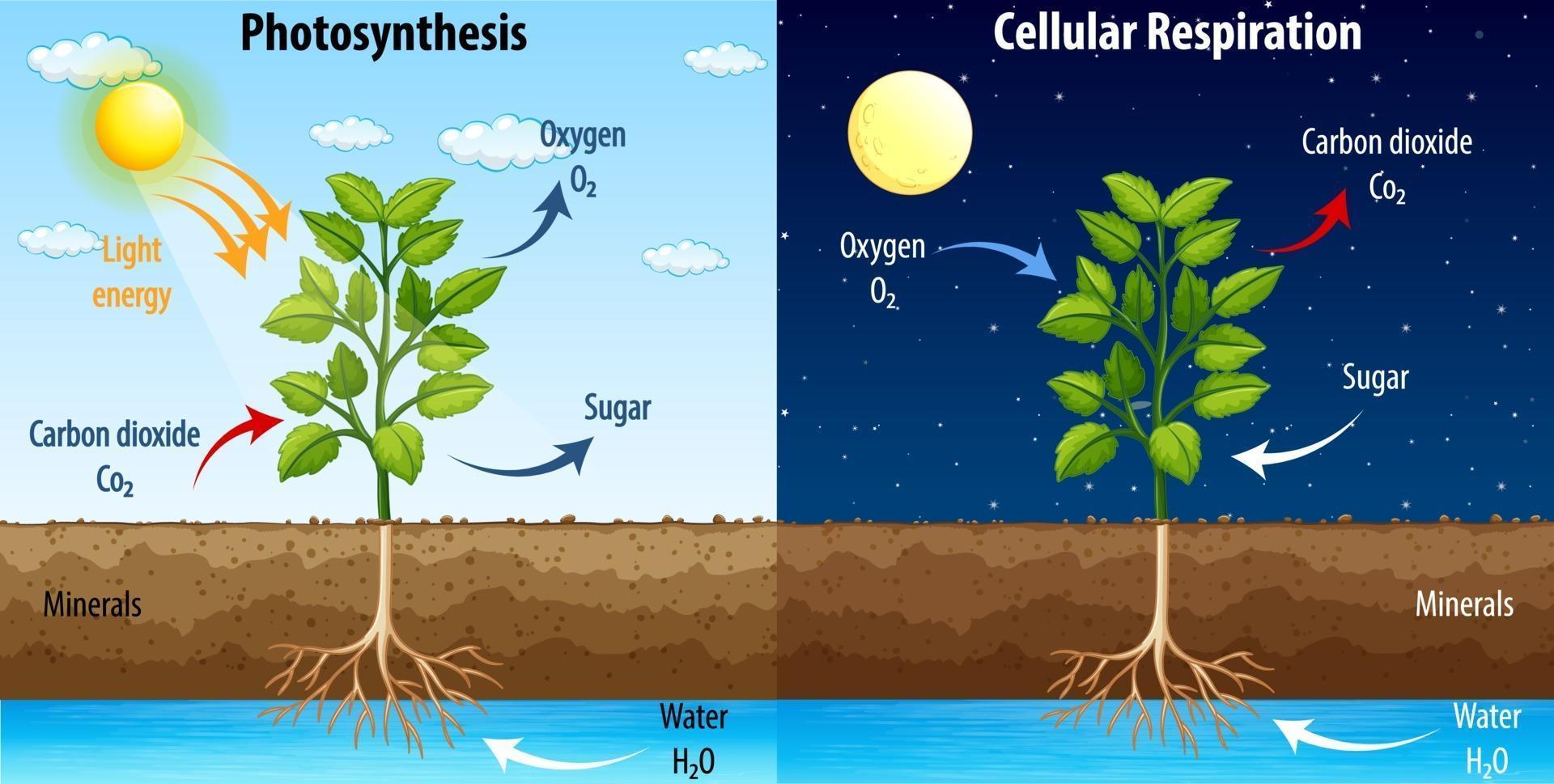
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Oxidation of food materials (breaking of C-C bonds of complex molecules) within the cell to release energy for ATP synthesis is called cellular respiration. This energy is used for absorption, transport, movement, reproduction, breathing etc. Ultimate source of food that is respired is photosynthesis.

Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes Vidyakul
The Process of Respiration in Plants During respiration, in different plant parts, significantly less exchange of gas takes place. Hence, each part nourishes and fulfils its own energy requirements. Consequently, leaves, stems and roots of plants separately exchange gases. Leaves possess stomata - tiny pores, for gaseous exchange.
Respiration in Plants Flashcards for NEET Biology
You will get all your answers in respiration in plants class 11 notes as it explains the process of release of energy from food in plants and its connection to breathing. Moreover, the whole process of how plants breathe in and what they breathe out is given here. Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.

Plant Respiration Experiment
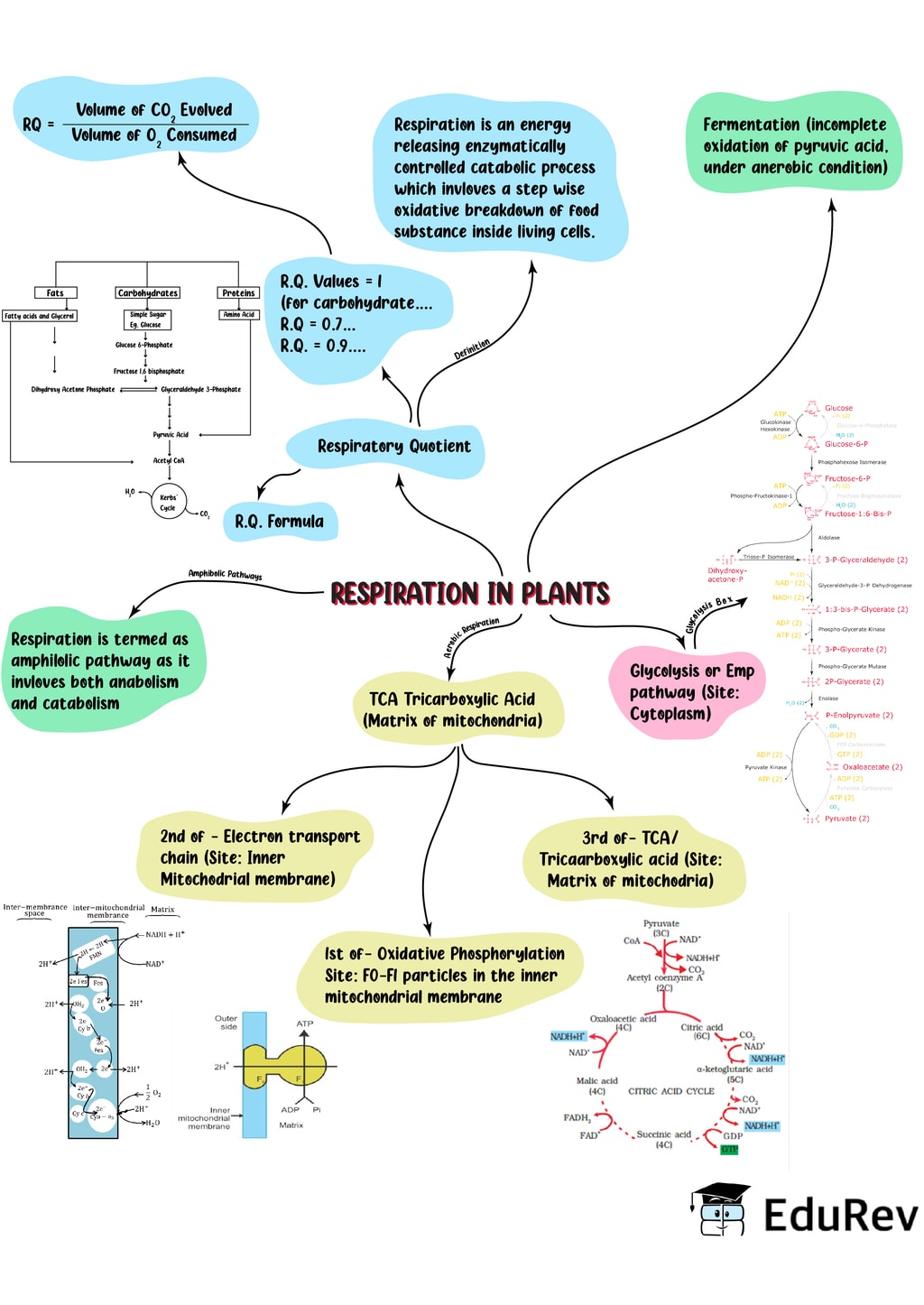
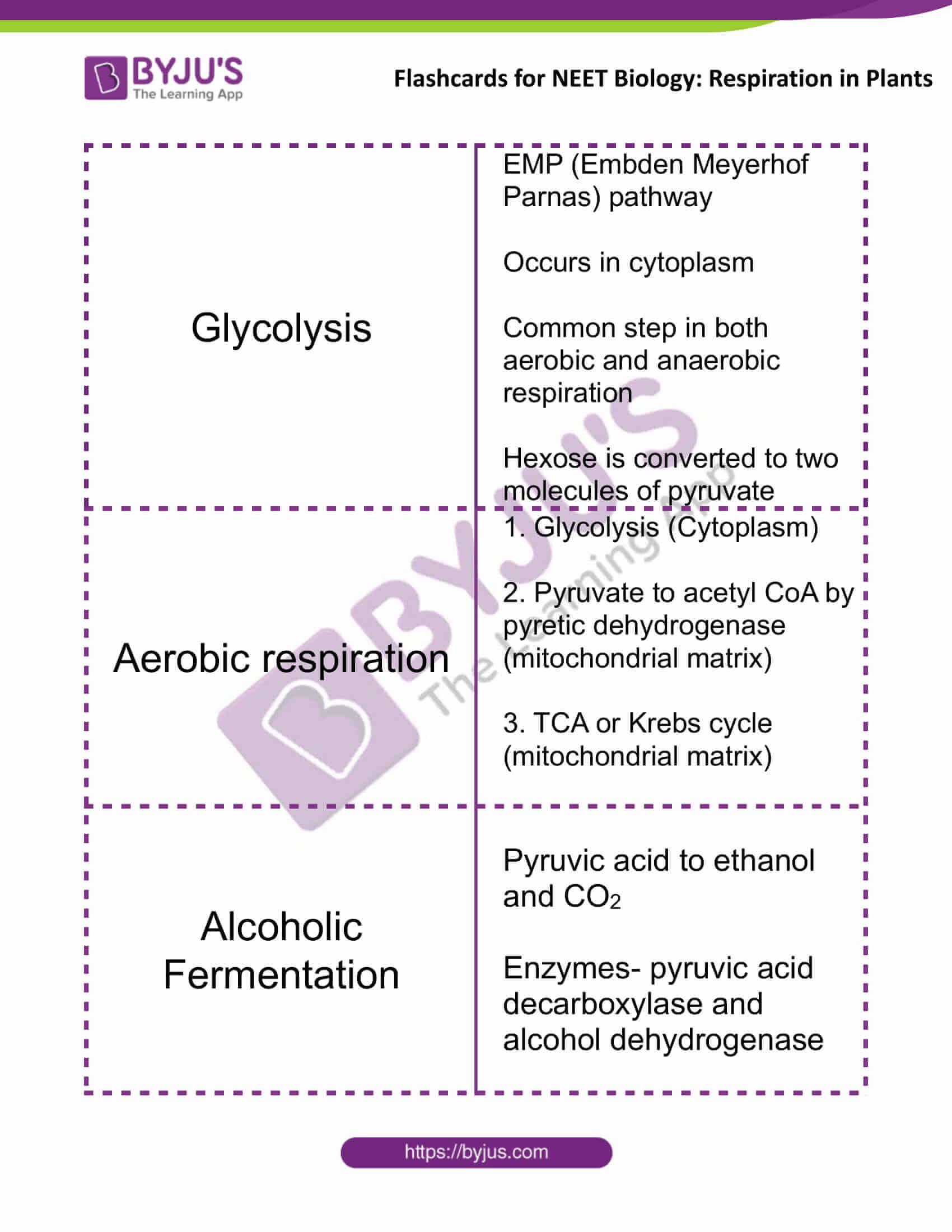
Steps of Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is an oxidative process where glucose gets converted into carbon dioxide, yielding ATP and NADH/FADH 2. The process takes place in four stages. 1) Glycolysis: Also known as the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway, it is the first step of cellular respiration.

Understanding plant respiration and heat stress Greenkeeping Magazine
Glycolysis The term glycolysis - (Greek words, glycols for sugar, and lysis for splitting). The scheme of glycolysis was given by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and J. Parnas, Hence glycolysis is called an EMP pathway. In anaerobic organisms, it is the only process in respiration. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in.

CBSE Notes Class 11 Biology Respiration in Plants AglaSem Schools
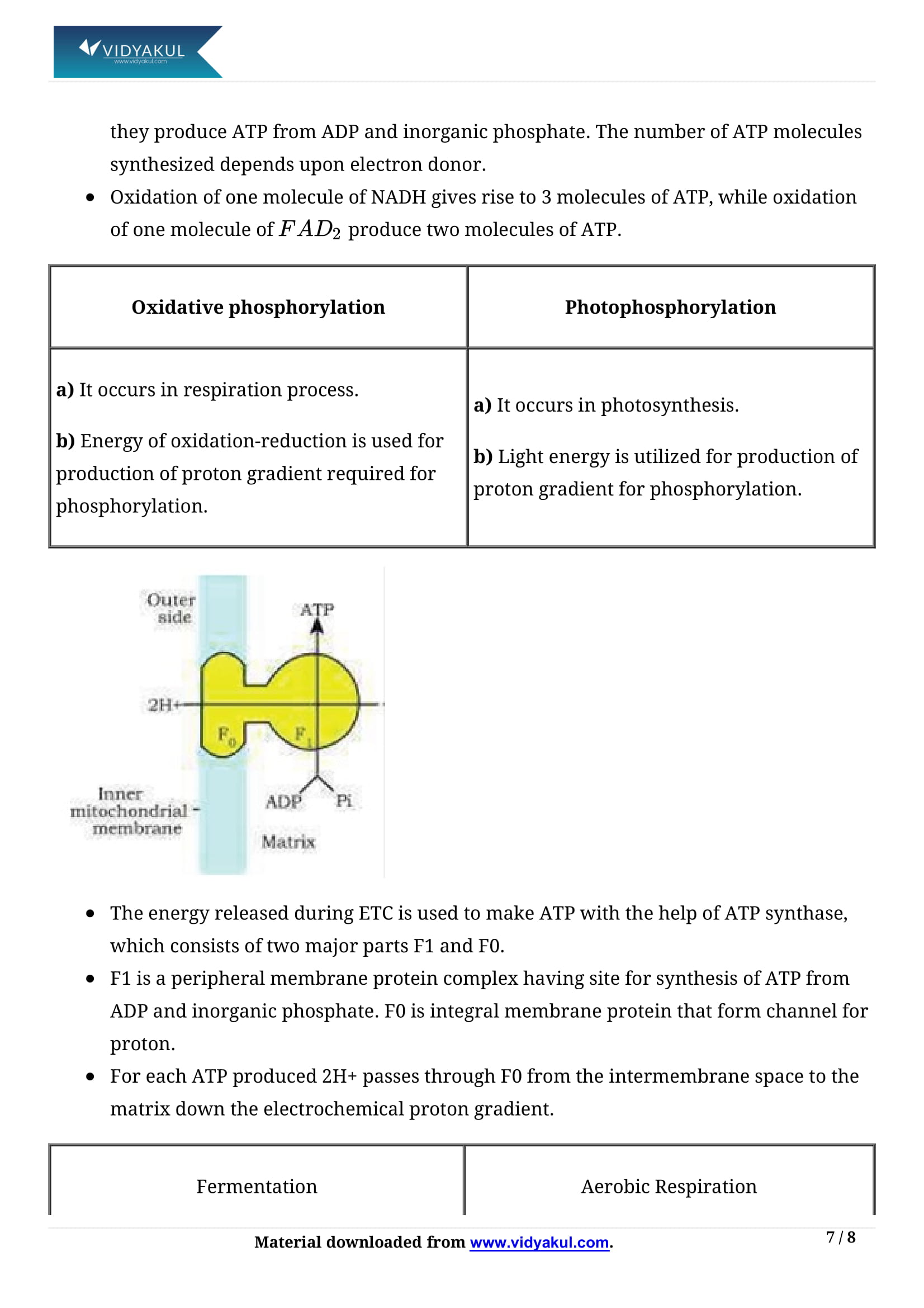
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS THE RESPIRATORY BALANCE SHEET Net gain of ATP from each glucose molecule is calculated based on the following assumptions: All steps in Glycolysis, TCA cycle & ETS occur sequentially and orderly. The NADH synthesised in glycolysis is transferred into mitochondria and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation.

Respiration in Plants One shot Video NEET Class 11 Plant Physiology
Significance of respiration: Respiration plays a significant role in the life of plants. The important ones are given below: (i) It releases energy, which is consumed in various metabolic processes necessary for life of plant. (ii) Energy produced can be regulated according to requirement of all activities. (iii) It converts in soluble foods.
Plant Respiration
ch-14.pmd CHAPTER 14 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS 14.1 Do Plants Breathe? 14.2 Glycolysis 14.3 Fermentation 14.4 Aerobic Respiration 14.5 The Respiratory Balance Sheet 14.6 Amphibolic Pathway 14.7 Respiratory Quotient All of us breathe to live, but why is breathing so essential to life? What happens when we breathe?
Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes Vidyakul
CBSE Notes For Class 11 CBSE Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 14: Respiration In Plants Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes - Chapter 14 Do Plants Breathe Respiration in Plants Important Questions for Respiration in Plants Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 11 Science Notes Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants