
Acute Phase Protein Protein Choices
The negative acute phase proteins are therefore described by some authors as 'acute booster reactants' (Ingenbleek and Young, 1994). In malnutrition and chronic infections the response of positive acute phase variables may be less evident (Morlese et al., 1998; Stephensen, 1999).

What Is The Difference Between Positive And Negative Acute Phase Proteins Relationship Between
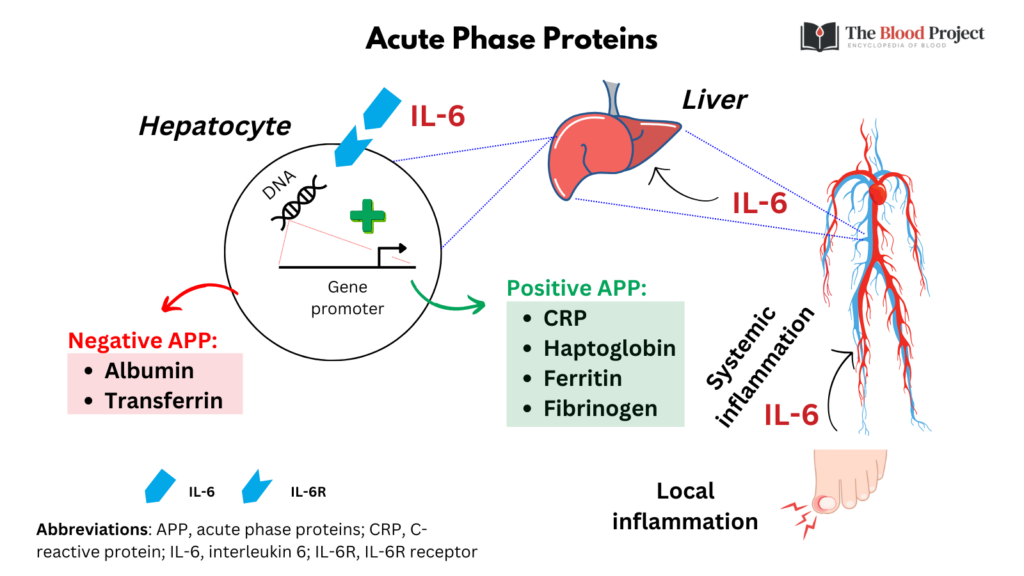
Inflammatory cells and red blood cells. Acute-phase proteins (APPs) are a class of proteins whose concentrations in blood plasma either increase (positive acute-phase proteins) or decrease (negative acute-phase proteins) in response to inflammation.This response is called the acute-phase reaction (also called acute-phase response).The acute-phase reaction characteristically involves fever.

Plasma indices of negative acute phase proteins (albumin, retinol, and... Download Scientific
A systemic acute phase reaction may develop during infection and inflammation, due to the action of peripherally liberated proinflammatory cytokines. Hepatic metabolism changes, and negative and positive acute phase proteins (APPs) can be measured in the blood: the APPs therefore represent appropriate analytes to assess health.

What is the Difference Between Positive and Negative Acute Phase Proteins Compare the
Since the discovery of C-reactive protein, acute-phase proteins have been invaluable tools at the bedside in a wide range of diseases, including Covid-19 and long Covid, 11-14,16 which points to.

Acutephase proteins MediGoo Health Medical Tests and Free Health Medical Information
Some acute-phase proteins increase during inflammation, while others,. Reference distributions for the negative acute-phase serum proteins, albumin, transferrin and transthyretin: a practical, simple and clinically relevant approach in a large cohort J Clin Lab Anal. 1999;13(6.

Positive & Negative Acute Phase Proteins (Note Those increased during inflammation are
Such proteins are termed either positive or negative acute phase reactants (APR), respectively. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), an indirect APR, reflects plasma viscosity and the presence of acute phase proteins, especially fibrinogen, as well as other influences, some of which are as yet unidentified [ 6 ].

P Proteins Astral Projection
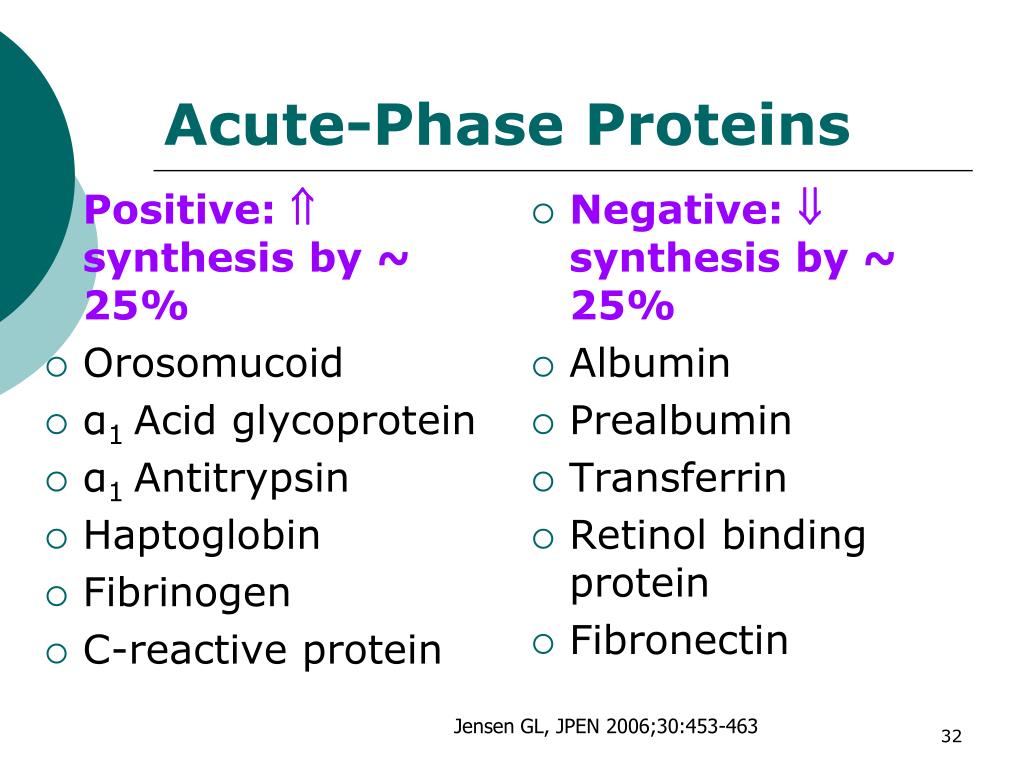
positive acute phase proteins; those that decline are called the negative acute-phase proteins (Tables 4 and 5, respectively). By definition, an acute-phase protein changes by at least 25% during inflammation. Alb, PAB, transferrin, and RBP are expected to return to normal as the inflammatory response resolves. It is clear that these negative.

Positive and Negative Acute phase Reactants Mnemonic
By definition, an acute-phase protein is one whose concentration in the plasma increases (for a 'positive' acute-phase protein) or decreases (for a 'negative' acute-phase protein) by at least 25 per cent during the acute phase (approximately the first 7 days) of inflammatory conditions (Morley and Kushner, 1982; Steel and Whitehead.

High Density Lipoproteins May Actually be Some Negative Acute Phase Proteins in the Plasma
Or third, albumin is known to be a negative acute phase protein, and as such hypoalbuminemia might represent an increased inflammatory status of the patient, potentially leading to poor outcomes. A thorough review of the literature reveals the fallacy of these arguments and fails to show a direct cause and effect between low albumin levels per.
Acute Phase Proteins Inflammation Markers NBG
Negative acute-phase proteins. The liver responds by producing a large number of APRs. At the same time, the production of a number of other proteins is reduced; these are therefore referred to as "negative" APPs. Negative APPs are albumin, transferring, transthyretin, transcortin, and retinol-binding protein.

Positive and negative acute phase proteins Download Table
During the acute phase response the demand for amino acids for synthesis of the positive acute phase proteins is markedly increased, which necessitates reprioritization of hepatic protein.
Acute Phase Proteins • The Blood Project
Acute phase proteins are produced in the liver in response to inflammatory cytokines. These proteins, such as α 2-macroglobulin and immunoglobulins, increase in inflammatory states, but albumin will decrease because albumin is a negative acute phase protein. This will result in a decreased albumin-to-globulin ratio.
PPT Labs Indicators for Nutritional Intervention PowerPoint Presentation ID6920966
The latter proteins have become known as the negative acute phase proteins. An acute phase response can be readily and reproducibly induced in experimental rats by subcutaneous injection of a small amount of mineral turpentine to produce a transient acute inflammation. The simultaneous decrease in the plasma concentration of negative acute.

(PDF) High and Low Density Lipoproteins May Be Negative Acute Phase Proteins of the Metabolic
The acute-phase proteins involved in free iron control include the circulating peptide hormone hepcidin, ferritin, haptoglobin, and hemopexin, which are up-regulated in the acute-phase reaction, whereas transferrin is a negative acute-phase protein that is down-regulated during the acute phase (Table 1). Hepcidin binds the transmembrane protein.

Negative acute phase proteins decrease in plasma concentration by greater than 25% in response to inflammation. This reduction can occur rapidly (within 24 hours) or may decrease gradually over a period of days. The two main negative acute phase proteins are albumin and transferrin. The mechanism by which their concentrations decrease is likely.

The acute phase response. An inflammatory stimulus results in... Download Scientific Diagram
Negative acute phase reactants are downregulated, and their concentrations decrease during inflammation. Positive acute phase reactants include procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, ferritin, fibrinogen, hepcidin, and serum amyloid A. Negative acute phase reactants include albumin, prealbumin, transferrin, retinol-binding protein, and antithrombin.