PPT Population Ecology Chapters 9 Miller 14 th Edition PowerPoint Presentation ID7085327
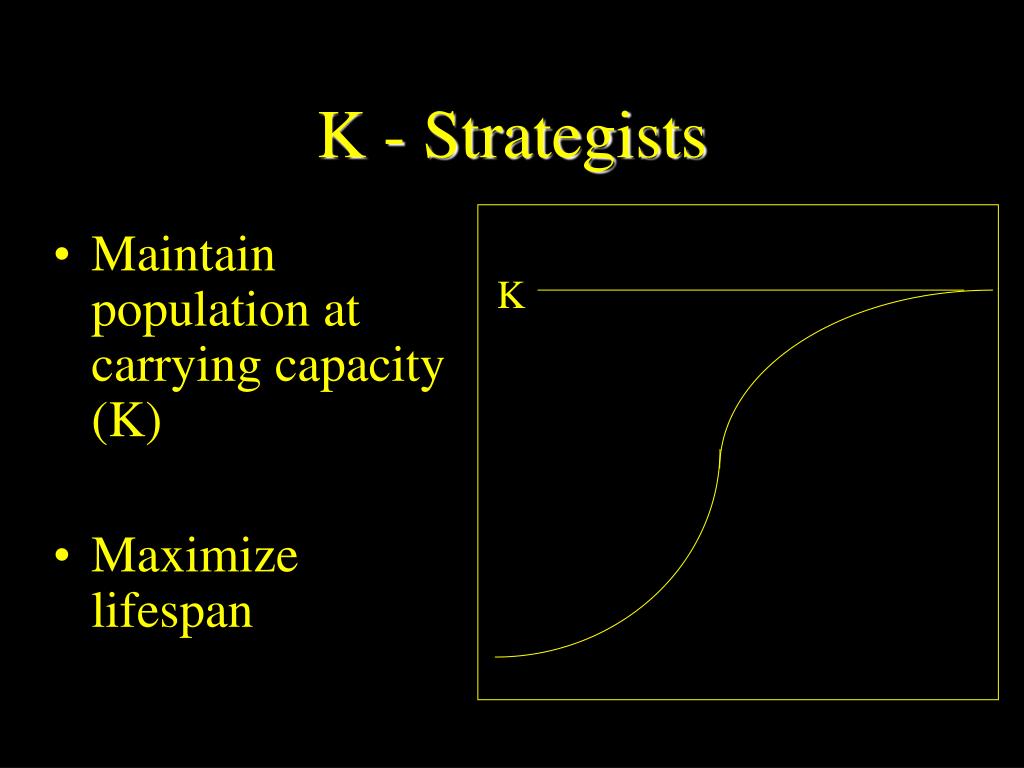
K-selected species, also calledK-strategist, species whose populations fluctuate at or near the carrying capacity (K) of the environment in which they reside. K-selected species possess relatively stable populations and tend to produce relatively low numbers of offspring; however, individual offspring tend to be quite large with high probability of survival in comparison with r-selected species.

Exploring The Reproductive Strategies Of Great White Sharks
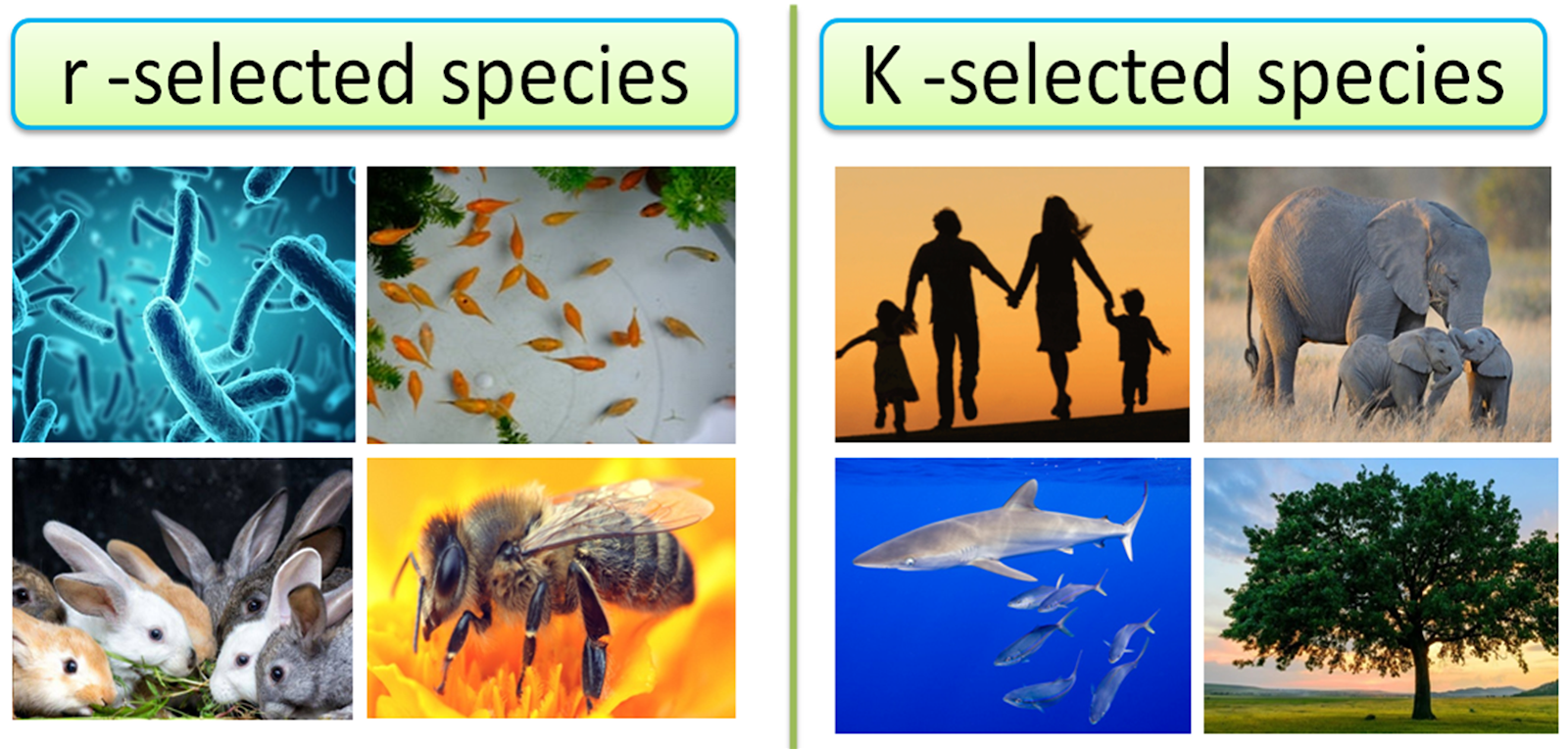
Common examples of k-strategists species include humans, lions and whales. R-strategists R-strategists "live" near the line of exponential growth . These organisms are nowhere near the carrying capacity, and can therefore afford to grow their population. In fact, they to.

Difference Between r Strategist and K Strategist Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
Abstract. Disturbance is a key factor shaping species abundance and diversity in plant communities. Here, we use a mechanistic model of vegetation diversity to show that different strengths of r- and K-selection result in different disturbance-diversity relationships. R- and K-selection constrain the range of viable species through the.

PPT Population Dynamics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID259317
The terms r-selection and K-selection are used by ecologists to describe the growth and reproduction strategies of organisms r-selected species have a high growth rate but low survivability ("cheap" offspring) K-selected species have a low growth rate but high survivability ("expensive" offspring) r-selection

Biological Terms AP Biology Summer Assignment
Category: Science & Tech Also called: K-strategist species carrying capacity See all related content → K-selected species, species whose populations fluctuate at or near the carrying capacity ( K) of the environment in which they reside.
.jpg)
Startups as an rstrategist species — Gavrilo Bozovic
Since r-strategist birth rates are so much higher than K-strategist birth rates, it follows that the vast majority of vertebrate individuals are r-strategists. So even if invertebrate r-strategists turned out to be insentient, r-strategists would still comprise the vast majority of sentient individuals born into the world.

PPT Bellwork PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID336319
K-strategists have stable populations that are close to K. There is nothing to be gained from a high r. The species will benefit most by a close adaptation to the conditions of its environment. Typically, K-strategists share these qualities: They are usually found in stable habitats. Most of the species in a mature forest will be K-strategists.

PPT Chapter 4 Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7026772
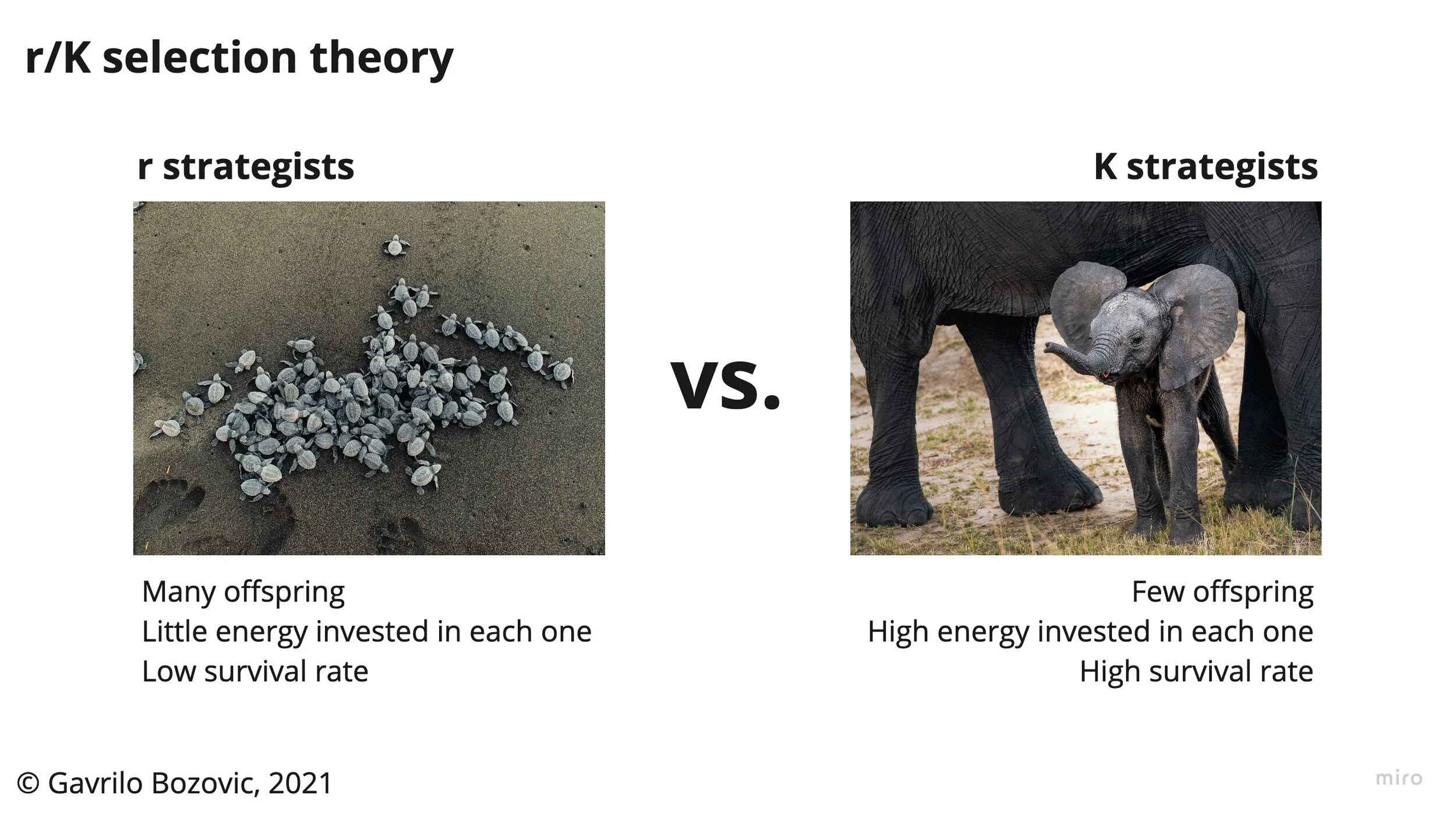
Consider the primary source of wild animal suffering: the r-strategy. Unlike K-strategist animals, who protect their genes by having few offspring and devoting considerable energy to each individual, r-strategist animals do the opposite: they protect their genes by producing many offspring but devoting little energy to each individual (MacArthur & Wilson, 1967; Pianka, 1970).
Difference between r and K Selection
Such species make up one of the two generalized life-history strategies posited by American ecologist Robert MacArthur and American biologist Edward O. Wilson; K -selected species —that is, species whose population sizes fluctuate at or near their carrying capacity ( K )—make up the second strategy.

PPT Population Dynamics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2385977
Whereas K-strategists perform well at densities close to the carrying capacity, the r-strategists do not. The properties of r- and K-selected microbial species given in Table 1 can be used both for selection of desired species (more details below) and for diagnostic purposes (Salvesen et al., 1999; Salvesen and Vadstein, 2000).
AP Biology Scavenger Hunt K Strategist
In ecology, r/K selection theory relates to the selection of combinations of traits in an organism that trade off between quantity and quality of offspring. The focus on either an increased quantity of offspring at the expense of individual parental investment of r -strategists, or on a reduced quantity of offspring with a corresponding.

Are Primates KSelected Or RSelected? Trust The Answer
K -strategists, including humans and most primates and zoo animals, exhibit Type I survivorship and tend to die when elderly. Species displaying Type II survivorship have an equal chance of survival at each age interval. Type II survivorship is highly theoretical, with few real-world examples.

45.3B Theories of Life History Biology LibreTexts
K-Strategists. Species with life history characteristics making them well suited for population stability and stable environments ("K" is an expression of carrying capacity of the environment). K-selected species represent an extreme on a continuum of life history characteristics, with r-selected species at the other end of the continuum.

PPT Population Ecology Chapters 9 Miller 14 th Edition PowerPoint Presentation ID7085327
Typical K-selected organisms are elephants, and humans. The table below summarizes some of the differences between r-organisms and K-organisms. It is not surprising that many organisms cannot be categorized neatly into this r vs. K scheme.

PPT Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5592518
3. Conduct classroom activities to help students identify K-strategists. You can give students a list of animals and ask them to research which ones are K-strategists. Alternatively, you can show them pictures of different animals and ask them to identify which ones are K-strategists. 4. Use multimedia tools such as videos, images, and.

Are Rabbits KSelected Or RSelected? Best 7 Answer
There are many examples of K-selected species. Whales and elephants are large-bodied mammalian K-selected species. Some trees (such as oaks) and reptiles (such as alligators) are also K-selected.