Steps in Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Biochemistry
Andrea Mauer. Andrea Mauer has been an educator for 17 years teaching animal behavior to pet training clients, K-12 core subjects in a homeschool setting, and middle school and high school science.

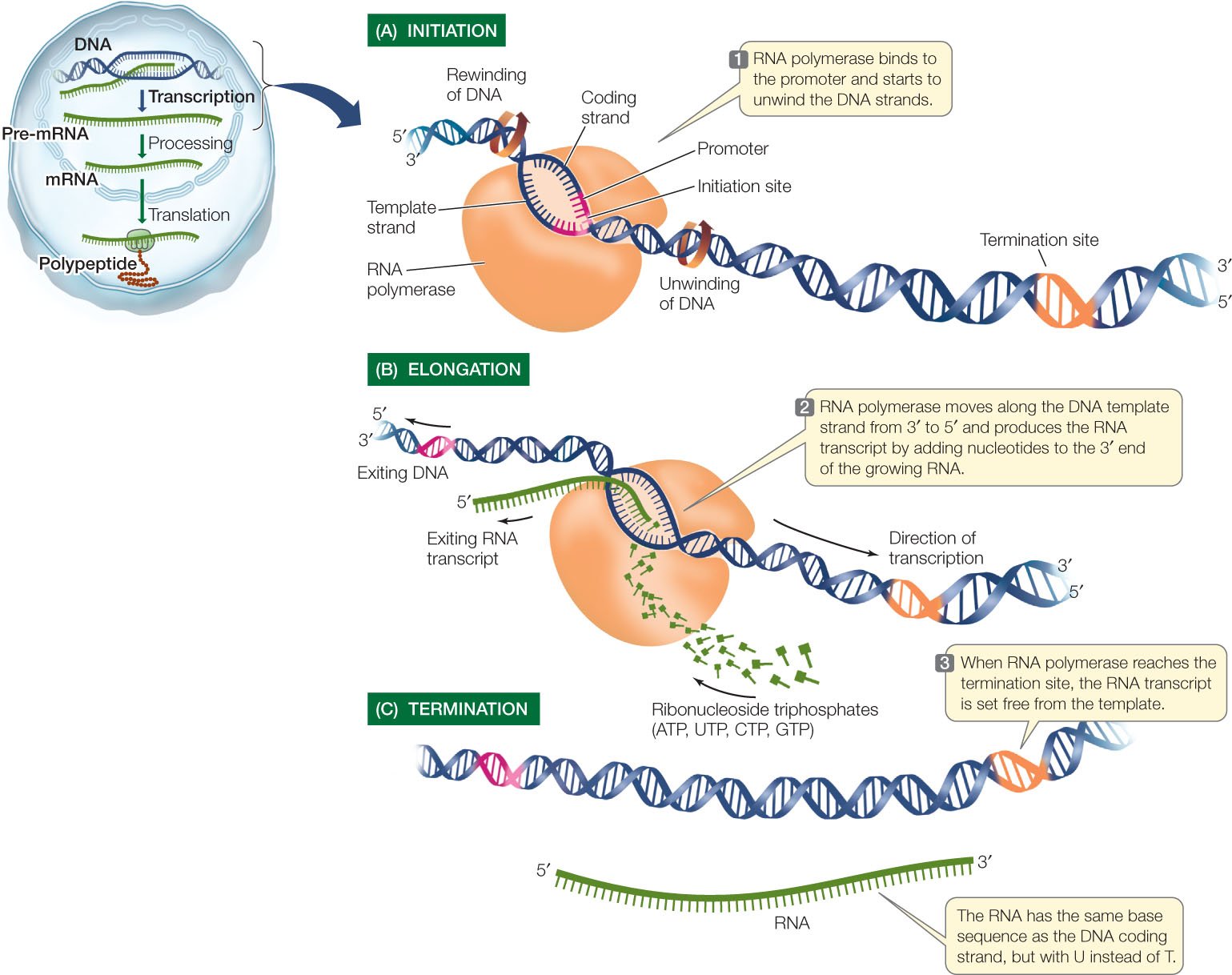
Biology Review Transcription in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Genetic Code. Genetic code consists of a sequence of nucleotide triplets called codons, each of which corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal.. The genetic code is universal, which means that the same codons represent the same amino acids across different organisms.
PPT Protein SynthesisTranscription PowerPoint Presentation ID4416235
The difference with prokaryotes. When proteins are made, they start off as chains of polypeptides. The study of how they come to fold into their correct three-dimensional structure is a.
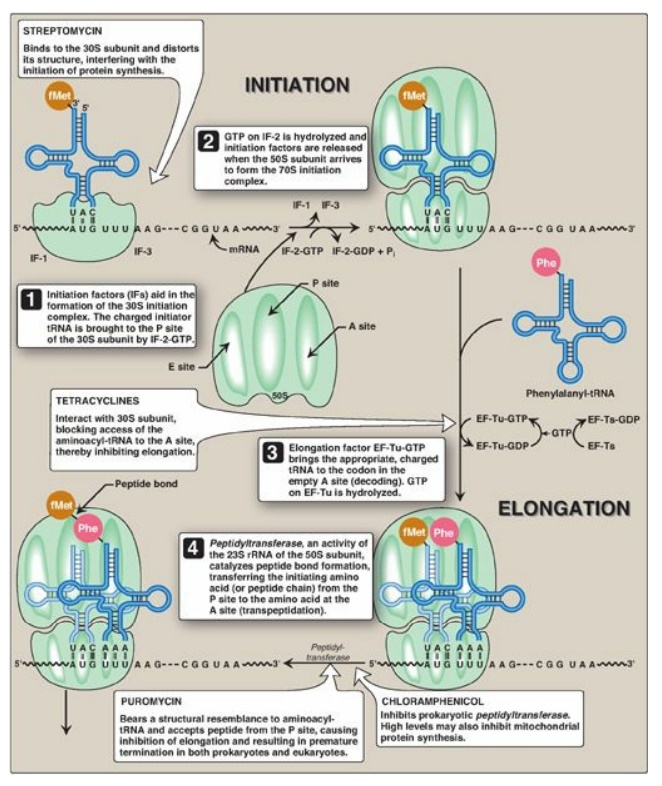
15. Elaborate how proteins' initiation, elongation, and termination happen in the ribosome with
The synthesis of proteins consumes more of a cell's energy than any other metabolic process. In turn, proteins account for more mass than any other macromolecule of living organisms. They perform virtually every function of a cell, serving as both functional (e.g., enzymes) and structural elements. The process of translation, or protein.
1.2. Transcripción en eucariotas
The polypeptide chain then folds and is post-translationally modified. Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes.

AB 2_2.3 Proteinbiosynthese und mehr vereinfacht, kurz und verständlich
Introduction. Cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) has become a fast-growing research area with high potential for industrial protein production. 1 The basic principle of cell-free systems was introduced by Eduard Buchner, developed not primarily to synthesize proteins but to convert sugar to ethanol and carbon dioxide in yeast extract. 2 More than 60 years later, Nirenberg and Matthaei.
Prokaryotic Transcription Enzymes, Steps, Significance
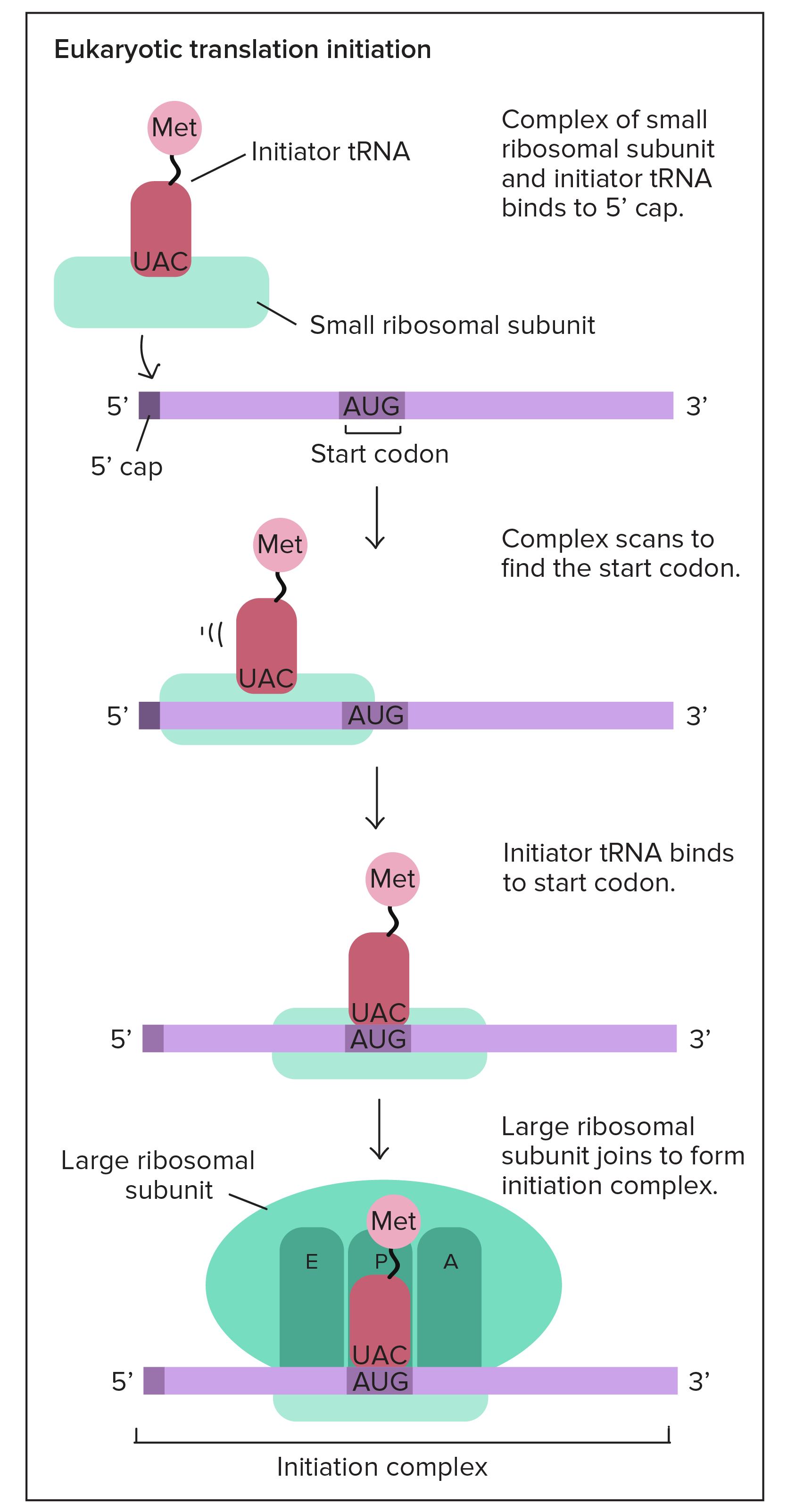
Abstract. This review summarizes our current understanding of the major pathway for the initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells, with a focus on recent advances. We describe the major scanning or messenger RNA (mRNA) m 7 G cap-dependent mechanism, which is a highly coordinated and stepwise regulated process that requires the.
Protein Synthesis Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes YouTube
Initiation of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes J Biochem. 1977 Jun;81(6):1p-14p. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131656.

tafelbild.ch Ein Tafelbild erklärt es einfach.
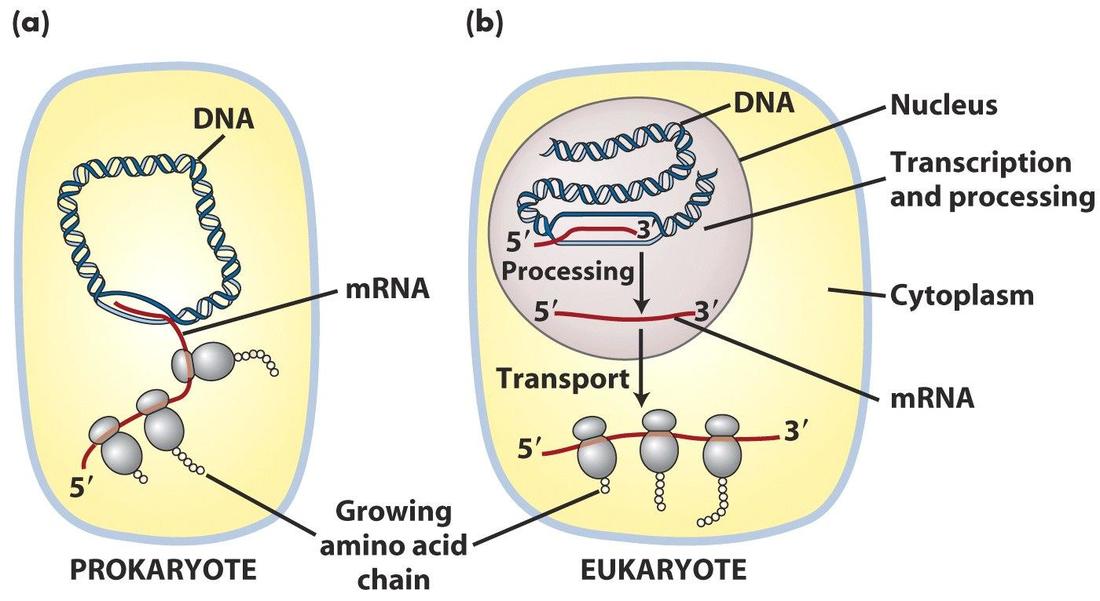
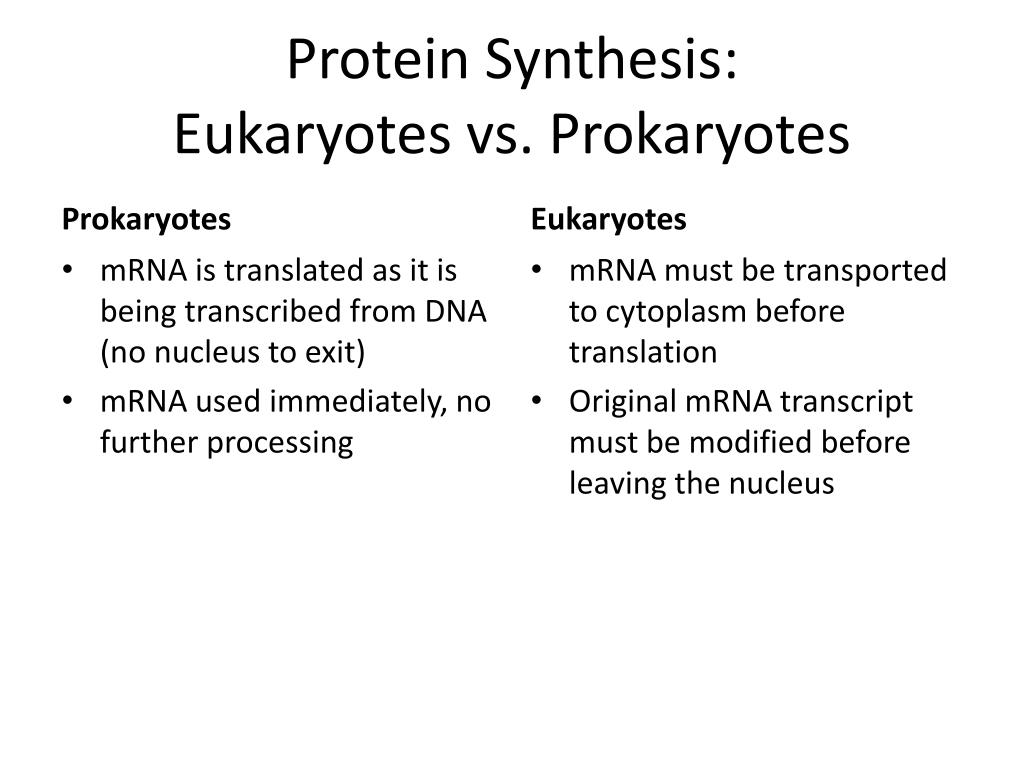
Eukaryotic synthesis is slower, but more precious. They can "check" the mRNA before it is translated into protein. Prokaryotes can translate mRNA into proteins while the DNA is being transcribed. Eukaryotes must end transcription of given segment, send it out of nucelus and only then translate it. Prokaryotic protein synthesis can be fairly.
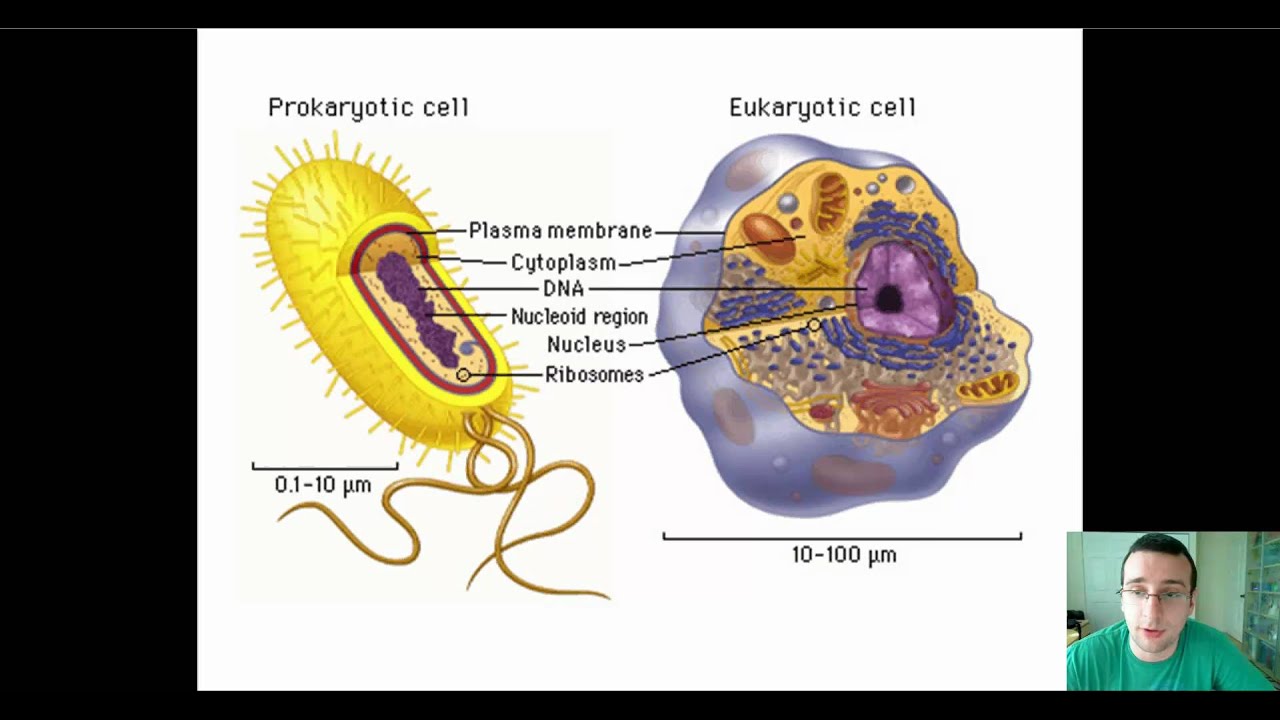
Compare Prokaryotic Cells to Eukaryote Cells Science News
E. coli extracts. One of the first CFPS systems was based on E. coli cell extracts, 3 and developments of this system have aimed at enhancing the yields of de novo synthesized proteins. The direct connection between protein yield and reaction life-time has led to the development of reaction methods that remove inhibitory byproducts such as inorganic phosphates by continuous flow 7 or passive.
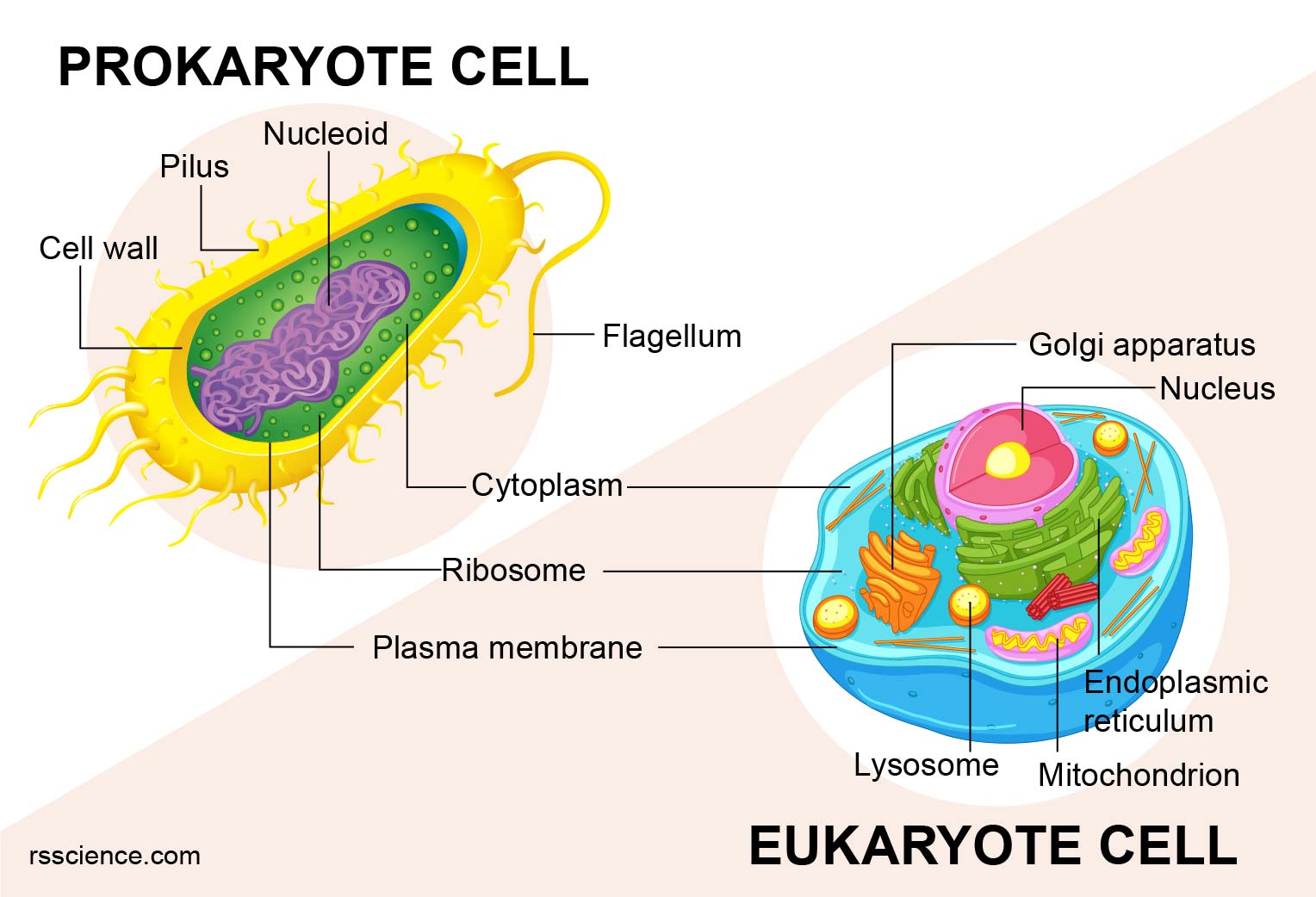
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes What are the Similarities, Differences, and Examples Rs' Science
Template generation. Templates for the synthesis of CYPs in cell-free systems were generated by Biocat GmbH. The protein encoding sequence and further regulatory factors for CAP-independent.
PPT Chapter 12 RNA and Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3961501
AboutTranscript. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles (such as the nucleus and mitochondria), while prokaryotic cells do not. DNA in eukaryotic cells is found inside the nucleus, while DNA in prokaryotic cells is located in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.

Protein Targetting Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Mutations AP Biology
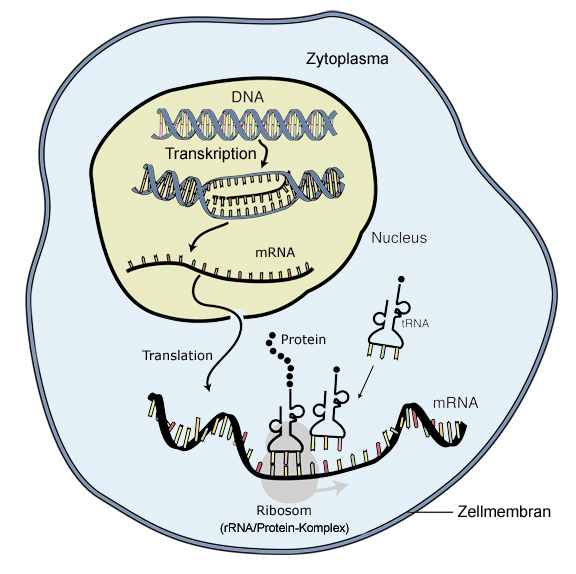
The translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: RNA --> Protein. It is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a protein. The translation is illustrated in Figure 6.4.6 6.4. 6. After mRNA leaves the nucleus, it moves to a ribosome, which consists of rRNA and proteins.

Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes. How is the process different in eukaryotes?
Protein Synthesis. Protein synthesis represents the major route of disposal of amino acids. Amino acids are activated by binding to specific molecules of transfer RNA and assembled by ribosomes into a sequence that has been specified by messenger RNA, which in turn has been transcribed from the DNA template.

Proteinbiosynthese SchulLV
Eukaryotic Protein Synthesis. mRNA molecules are polycistronic and contain the coding sequences of several genes in a metabolic pathway. mRNA molecules are monocistronic and contain the coding sequence of only one peptide. Neither splicing nor processing of the mRNA transcript occurs. The main mRNA transcript goes through processing and.

Transcription this is the first step in protein sequenc...
The process of protein synthesis in E. coli involves the following steps: 1. Transcription: The partial uncoiling of two DNA strands occurs. This is followed by the production of single stranded mRNA on one of the two DNA strands. The messenger RNA complement is made in accordance with base pairing rules.