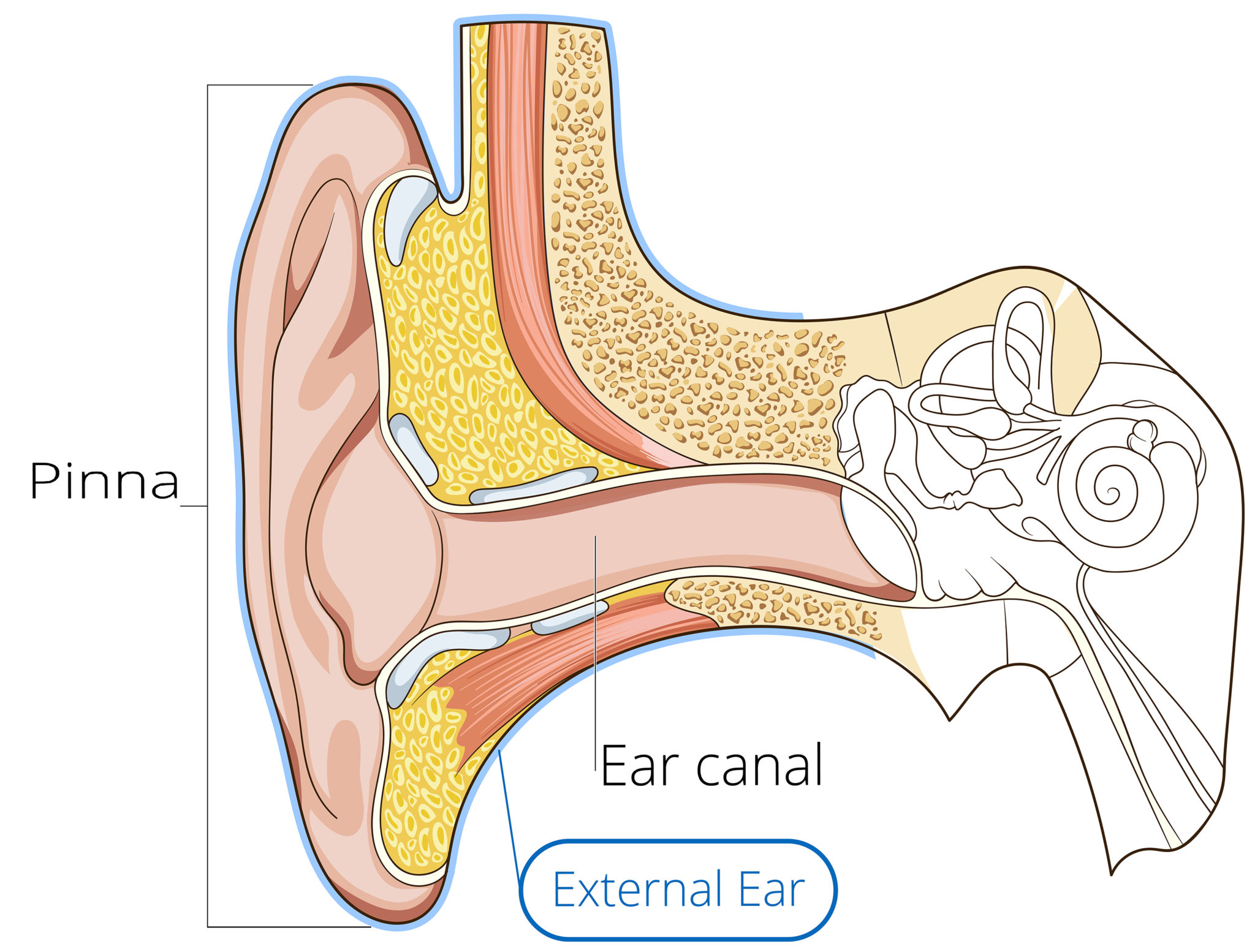
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
Helix: The outermost curvature of the ear, extending from where the ear joins the head at the top to where it meets the lobule. The helix begins the funneling of sound waves into the ear; Fossa, superior crus, inferior crus, and antihelix: These sections make up the middle ridges and depressions of the outer ear. The superior crus is the first ridge that emerges moving in from the helix.

The human ear structure and how it works Connect Hearing
Human ear Contents [ hide] Human ear Parts of the ear External (Outer) Ear Middle Ear Internal (Inner) Mechanism for Hearing Ear problems Swimmer's ear Causes of Swimmer's ear How the swimmer's ear occurs Risk factors for swimmer's ear Symptoms of Swimmer's ear When to see a doctor Complications of Swimmer's ear Prevention of Swimmer's ear
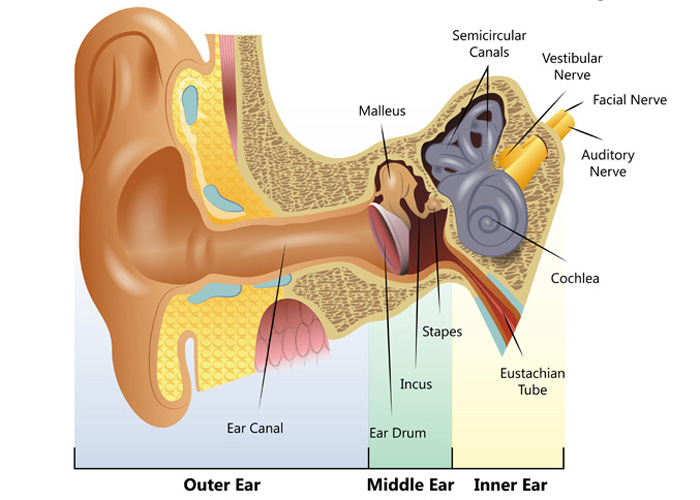
Understanding how the ear works Hearing Link Services
The ear also helps in balancing the body. The human ear allows us to feel the effect of gravity that is known as stationary balance and it also helps to feel the acceleration that is known as dynamic balance. The utricle and saccule provide a static balance. Dynamic balance is provided by semi-circular canals.

Diagram Of A Human Ear Vector Illustration Of Diagram Of Human Ear Anatomy Royalty Free Ear
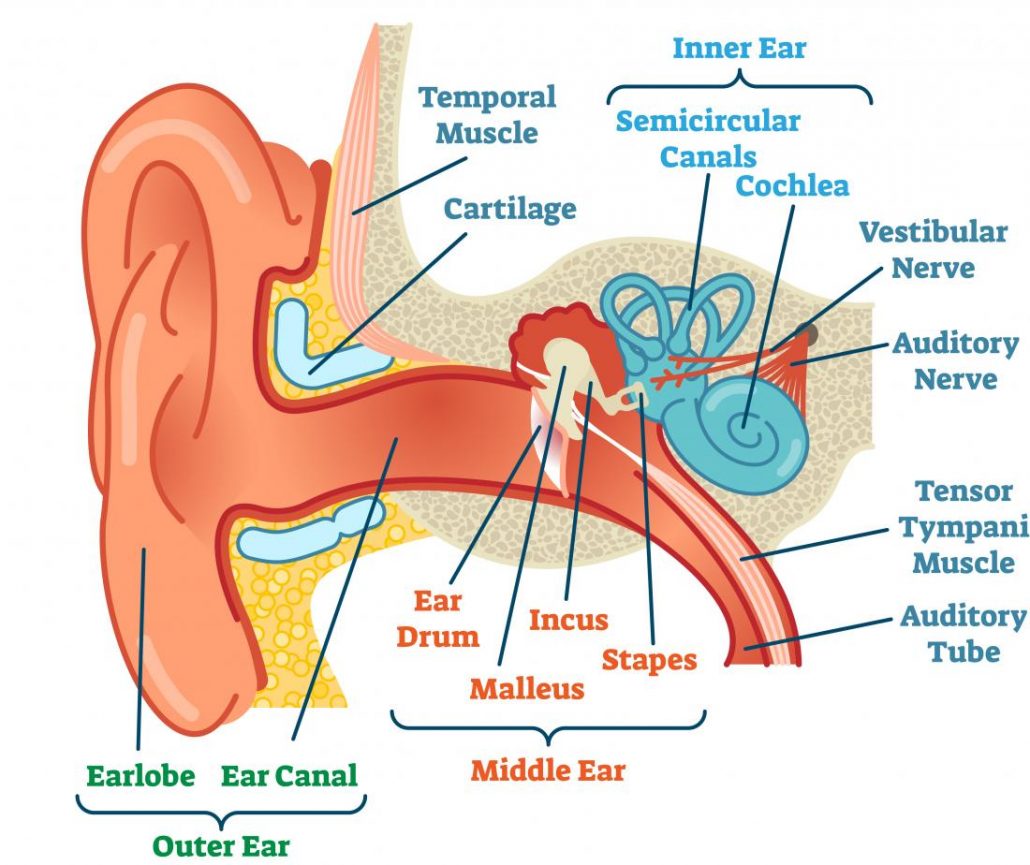
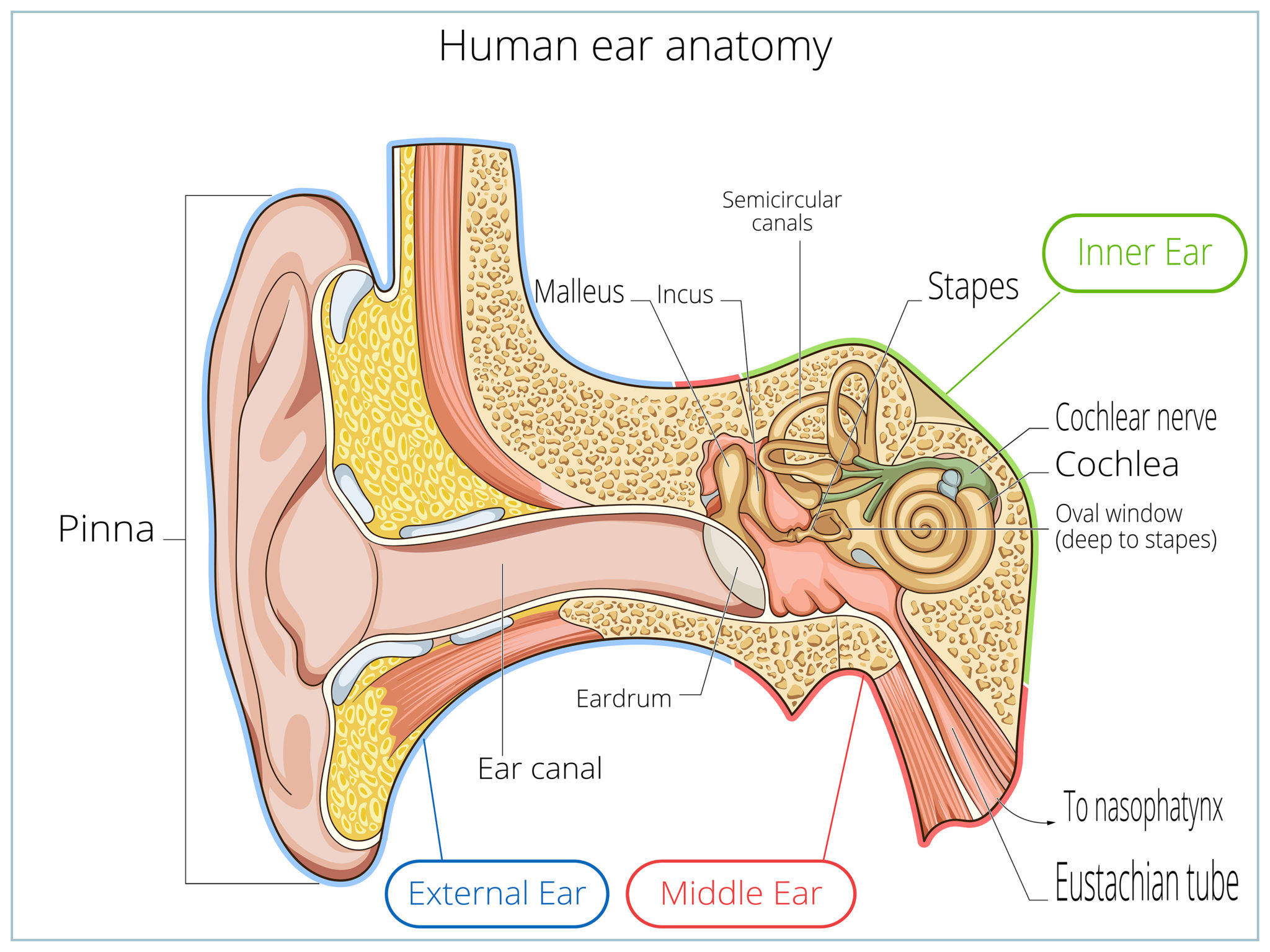
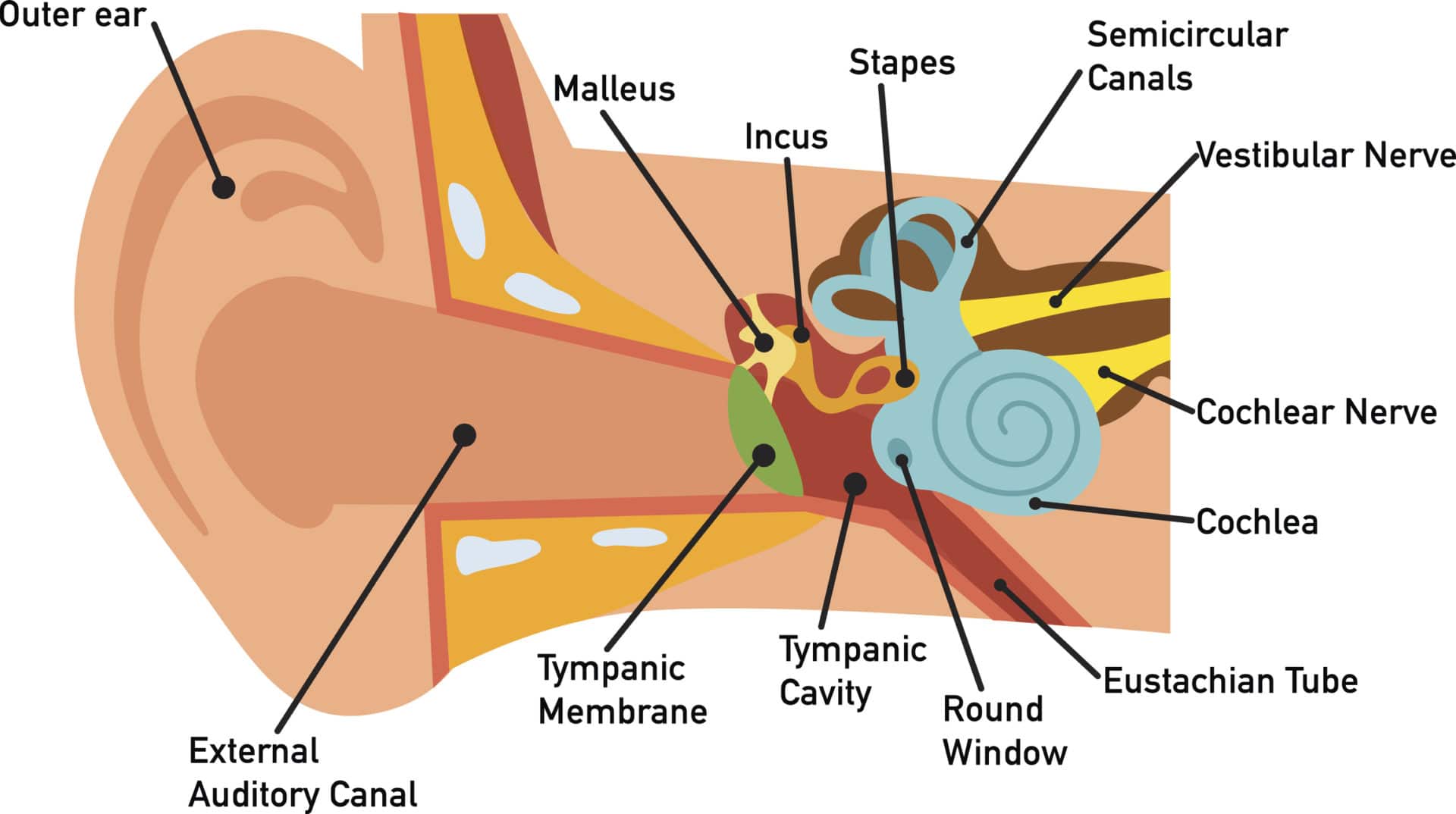
The ear is anatomically divided into three portions: External ear Middle ear Internal ear This mixture of bones, nerves, vessels, membranes, and muscles that make up the ear will be described in this article. Contents External ear Auricle External acoustic meatus Tympanic membrane Muscles of the external ear Vasculature of the external ear

The Anatomy of the Outer Ear Health Life Media
Structure The ear is made up of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The inner ear consists of the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth comprises three components: Cochlea: The cochlea is made of a hollow bone shaped like a snail and divided into two chambers by a membrane.
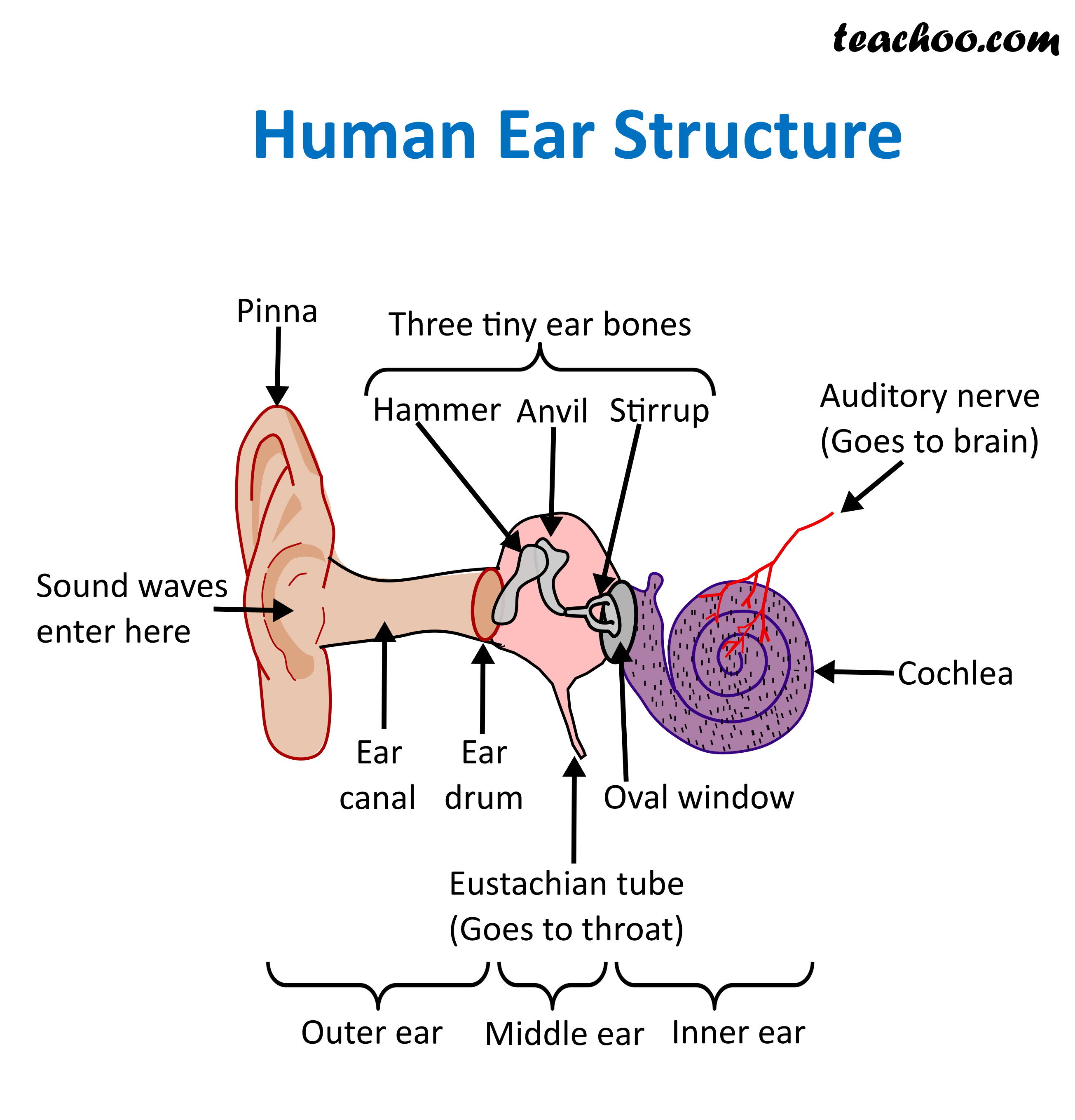
Structure and Function of Human Ear with Diagram Teachoo
human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). Understand the science of hearing and how humans and other mammals perceive sound How humans and other mammals perceive sound.

15.3 Hearing Anatomy & Physiology
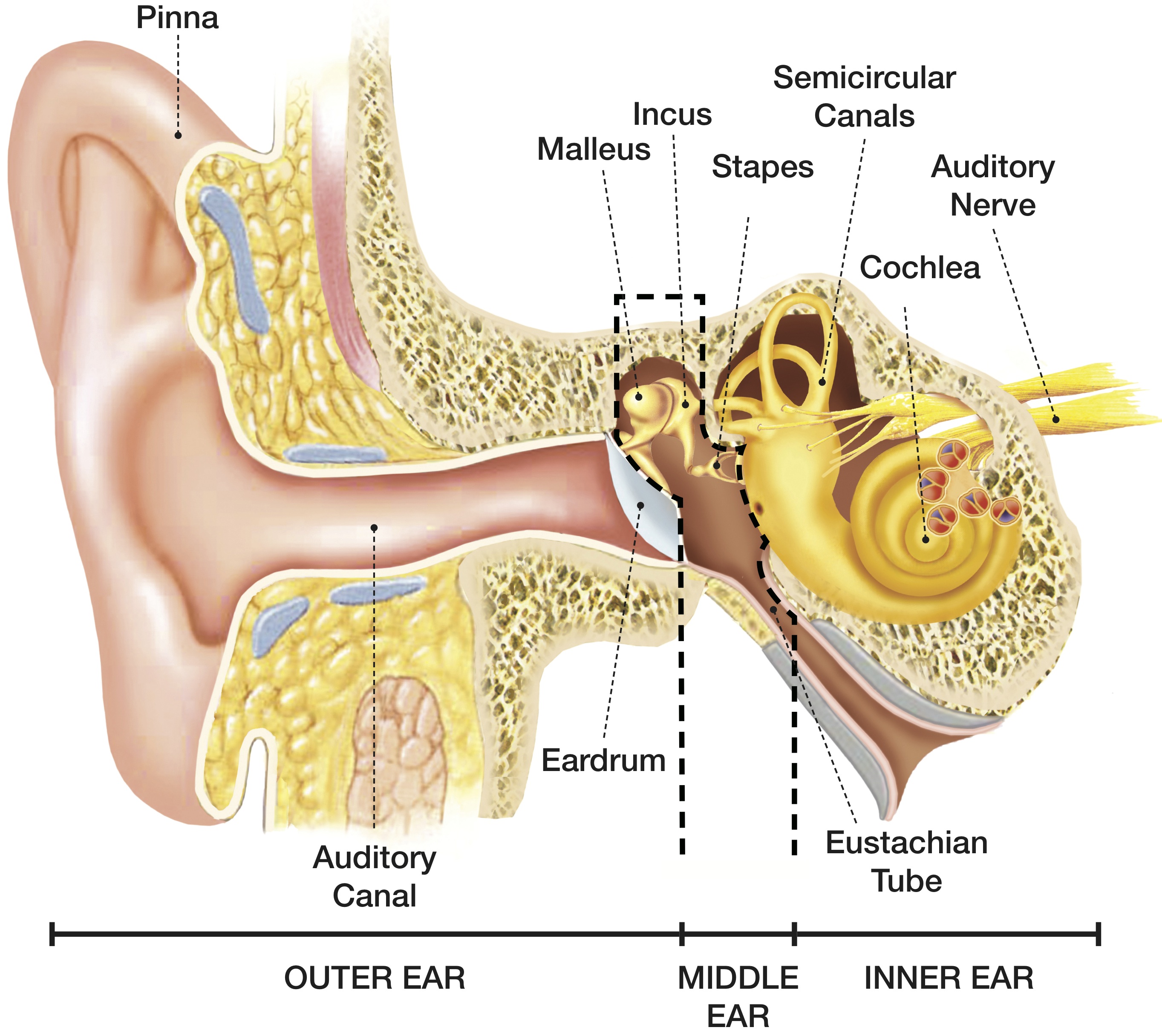
What is the main function of the ear? Your ears have two main functions: hearing and balance. Hearing: When sound waves enter your ear canal, your tympanic membrane (eardrum) vibrates. This vibration passes on to three tiny bones (ossicles) in your middle ear. The ossicles amplify and transmit these sound waves to your inner ear.
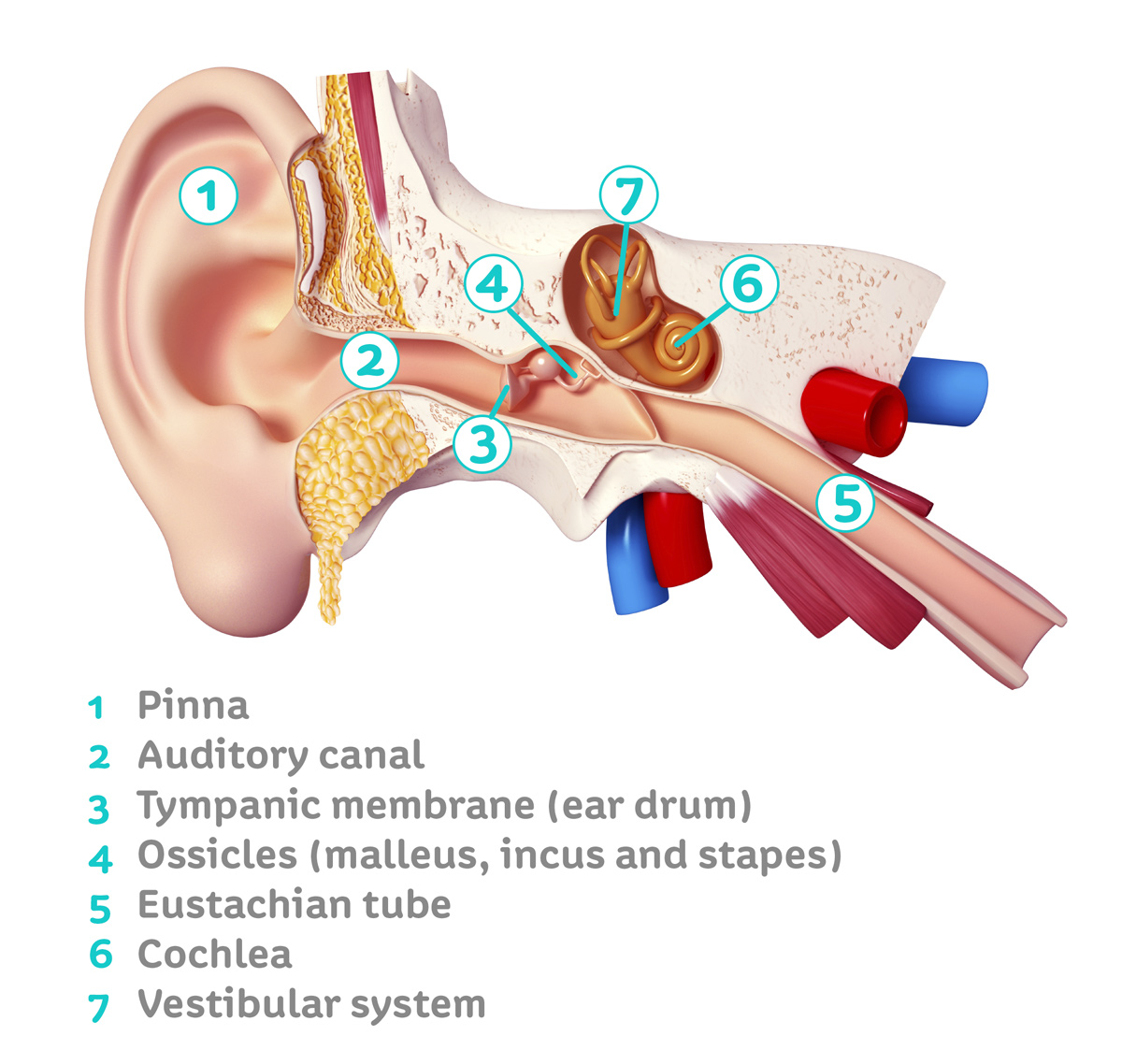
The Ear — Summerlin Audiology
The Anatomy of the Ear Organs of human hearing are located on either side of the head By Mark Gurarie Updated on June 07, 2022 Medically reviewed by John Carew, MD Table of Contents Anatomy Function Associated Conditions Tests Essential for hearing and balance, each ear has an intricate structure of bones, nerves, and muscles.
How The Ear Works Step by Step Brief Explanation
A canal that links the middle ear with the back of the nose. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure in the middle ear. Equalized pressure is needed for the correct transfer of sound waves. The eustachian tube is lined with mucous, just like the inside of the nose and throat. Inner ear, consisting of: Cochlea.
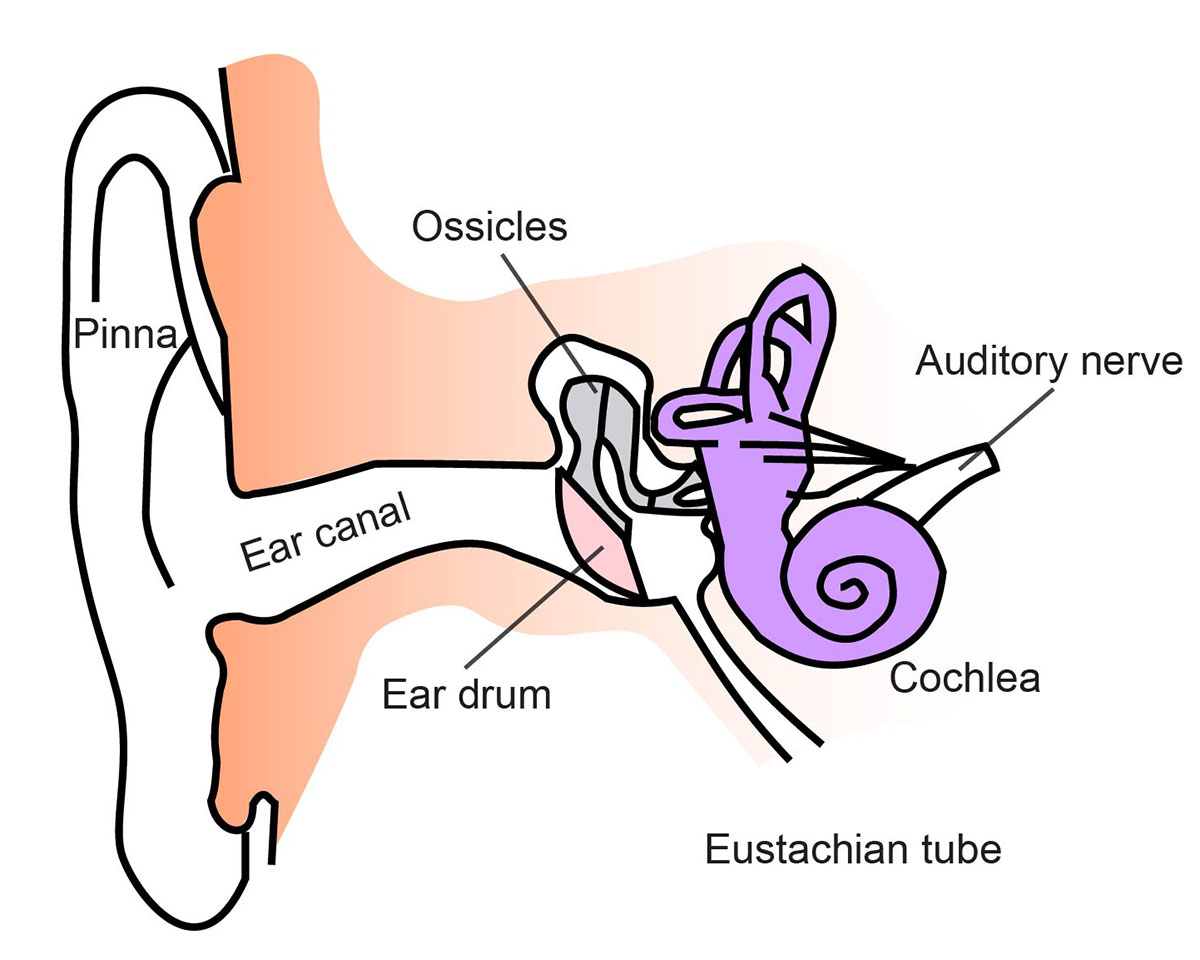
Hearing Sense Ask A Biologist
The human ear consists of three parts—the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. [6] The ear canal of the outer ear is separated from the air-filled tympanic cavity of the middle ear by the eardrum.

Human Ear Anatomy Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear Problems
External acoustic meatus. The ear canal, also called the external acoustic meatus, is a passage comprised of bone and skin leading to the eardrum. The ear is comprised of the ear canal (also known.
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
The Human Ear www.TurnItToTheLeft.com. If the noise is too loud, walk away, turn it down (Turn it to the Left), or use ear plugs. pinna ear canal ear drum hammer anvil stirrup Eustachian tube (connects to the nose) cochlea semicircular canals nerves (connect to the brain) Directions: Color in the diagram below using a different color for.
Ear Diagram Helix Human Anatomy diagram
Ear Anatomy, Diagram & Pictures | Body Maps Human body Head Ear Ear The ears are organs that provide two main functions — hearing and balance — that depend on specialized receptors called.
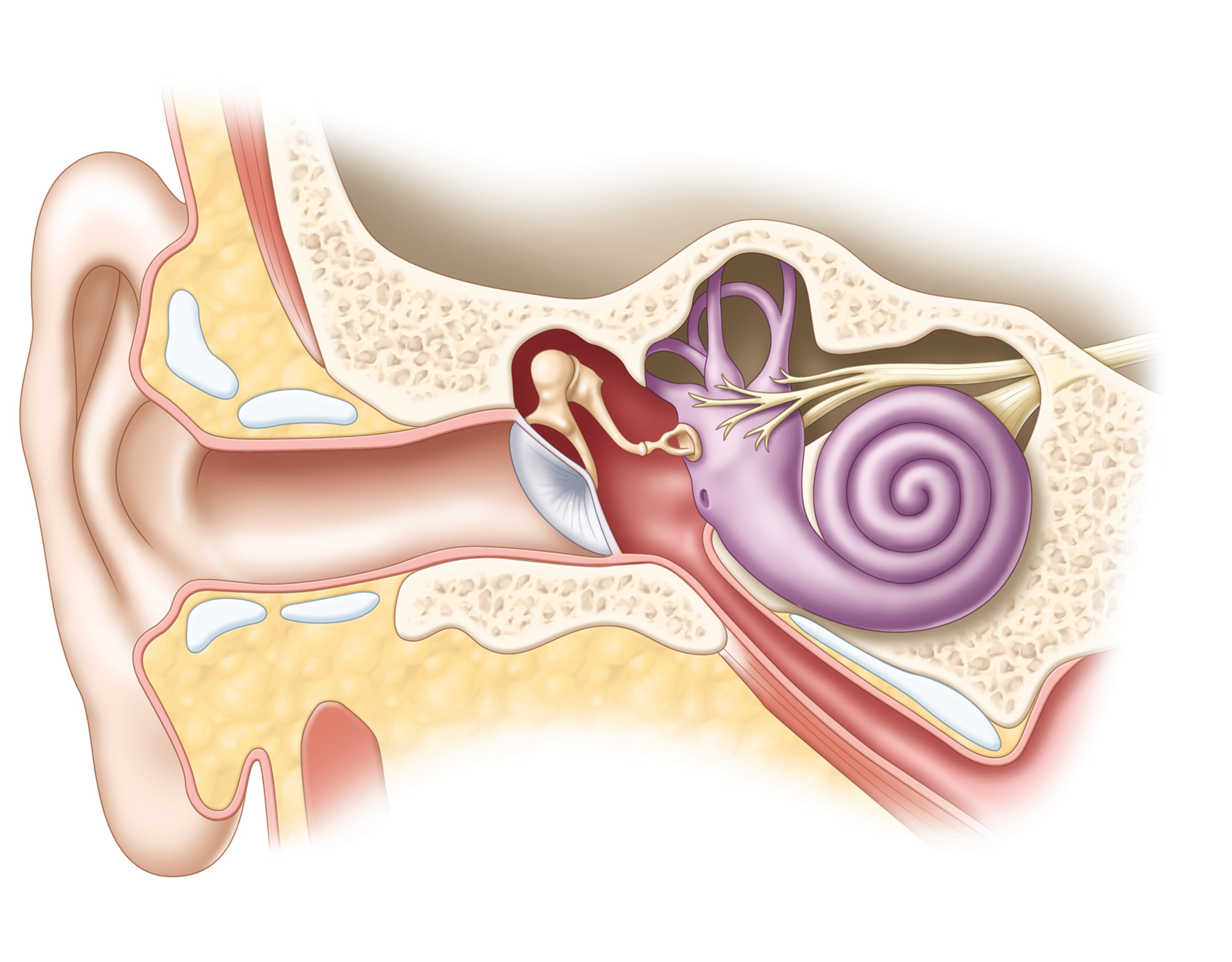
Inner Ear anatomy Christine Kenney
Diagram of Ear Human ear is a sense organ responsible for hearing and body balance. The outer ear receives the sound waves and transmits them down the ear canal to the eardrum. This causes the eardrum to vibrate and sound is produced. The diagram of the ear is important from Class 10 and 12 perspectives and is usually asked in the examinations.
How You Hear Northland Audiology
The human ear consists of three parts: External ear Middle ear Internal ear Human Ear Parts The human ear parts are explained below: External Ear The external ear is further divided into the following parts: Auricle (Pinna) The auricle comprises a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by a layer of skin.
How We Hear Hearing Associates, Inc.
Let's explore how human ears work. More free lessons & practice on this chapter-https://www.khanacademy.org/science/in-in-class9th-physics-india/in-in-sound-.